Conducting polymer hydrogels based on supramolecular strategies for wearable sensors
- PMID: 39439497
- PMCID: PMC11491309
- DOI: 10.1002/EXP.20220167
Conducting polymer hydrogels based on supramolecular strategies for wearable sensors
Abstract
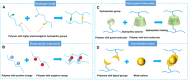
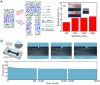
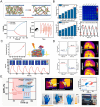
Conductive polymer hydrogels (CPHs) are gaining considerable attention in developing wearable electronics due to their unique combination of high conductivity and softness. However, in the absence of interactions, the incompatibility between hydrophobic conductive polymers (CPs) and hydrophilic polymer networks gives rise to inadequate bonding between CPs and hydrogel matrices, thereby significantly impairing the mechanical and electrical properties of CPHs and constraining their utility in wearable electronic sensors. Therefore, to endow CPHs with good performance, it is necessary to ensure a stable and robust combination between the hydrogel network and CPs. Encouragingly, recent research has demonstrated that incorporating supramolecular interactions into CPHs enhances the polymer network interaction, improving overall CPH performance. However, a comprehensive review focusing on supramolecular CPH (SCPH) for wearable sensing applications is currently lacking. This review provides a summary of the typical supramolecular strategies employed in the development of high-performance CPHs and elucidates the properties of SCPHs that are closely associated with wearable sensors. Moreover, the review discusses the fabrication methods and classification of SCPH sensors, while also exploring the latest application scenarios for SCPH wearable sensors. Finally, it discusses the challenges of SCPH sensors and offers suggestions for future advancements.
Keywords: conductive polymer; hydrogel; supramolecular interaction; wearable sensor.
© 2024 The Author(s). Exploration published by Henan University and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

















References
-
- Wen F., He T., Liu H., Chen H.‐Y., Zhang T., Lee C., Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105155.
-
- Ling Y., An T., Yap L. W., Zhu B., Gong S., Cheng W., Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1904664. - PubMed
-
- Meng K., Xiao X., Liu Z., Shen S., Tat T., Wang Z., Lu C., Ding W., He X., Yang J., Chen J., Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202478. - PubMed
-
- Yang T., Xie D., Li Z., Zhu H., Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2017, 115, 1.
-
- Mamun M. a. A., Yuce M. R., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005703.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
