Development of acute kidney injury following repair of Stanford type A aortic dissection is associated with increased mortality and complications: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis
- PMID: 39439591
- PMCID: PMC11495731
- DOI: 10.1097/XCE.0000000000000314
Development of acute kidney injury following repair of Stanford type A aortic dissection is associated with increased mortality and complications: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis
Abstract
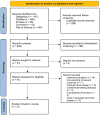
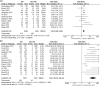
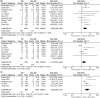
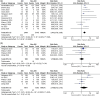
Acute kidney injury (AKI) frequently complicates the repair of Stanford type A aortic dissection (TAAD). This systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression analysis aimed to elucidate the prognostic impact of AKI in these patients. A literature search in PubMed, EMBASE, and Google Scholar identified relevant studies on the predictors and outcomes of AKI following TAAD repair. The primary endpoint was 30-day mortality; secondary endpoints included stroke, dialysis/continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), and other complications. Random-effects meta-analyses were used, with significance set at P < 0.05. Twenty-one studies (10 396 patients) were analyzed. AKI was associated with higher risks of 30-day mortality (risk ratio = 3.98), stroke (risk ratio = 2.05), dialysis/CRRT (risk ratio = 32.91), cardiovascular (risk ratio = 2.85) and respiratory complications (risk ratio = 2.13), sepsis (risk ratio = 4.92), and re-exploration for bleeding (risk ratio = 2.46). No significant differences were noted in sternal wound infection, tracheostomy, paraplegia, or hepatic failure. AKI significantly increases mortality, morbidity, hospital, and ICU stay duration in TAAD repair patients.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; aortic dissection; cardiology; meta-analysis; mortality; prevention.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Daily PO, Trueblood HW, Stinson EB, Wuerflein RD, Shumway NE. Management of acute aortic dissections. Ann Thorac Surg 1970; 10:237–247. - PubMed
-
- Pape LA, Awais M, Woznicki EM, Suzuki T, Trimarchi S, Evangelista A, et al. . Presentation, diagnosis, and outcomes of acute aortic dissection: 17-year trends from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015; 66:350–358. - PubMed
-
- Parikh N, Trimarchi S, Gleason TG, Kamman AV, di Eusanio M, Myrmel T, et al. . Changes in operative strategy for patients enrolled in the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection interventional cohort program. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017; 153:S74–S79. - PubMed
-
- Sasabuchi Y, Kimura N, Shiotsuka J, Komuro T, Mouri H, Ohnuma T, et al. . Long-term survival in patients with acute kidney injury after acute type A aortic dissection repair. Ann Thorac Surg 2016; 102:2003–2009. - PubMed
-
- Collins JS, Evangelista A, Nienaber CA, Bossone E, Fang J, Cooper JV, et al. . Differences in clinical presentation, management, and outcomes of acute type A aortic dissection in patients with and without previous cardiac surgery. Circulation 2004; 110(11 Suppl 1):II237–II242. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
