Induction of interleukin-6 by SPZ1-mediated Wnt5a signaling boosts progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- PMID: 39440046
- PMCID: PMC11493014
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.99648
Induction of interleukin-6 by SPZ1-mediated Wnt5a signaling boosts progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
Abstract
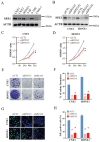
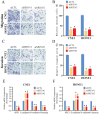
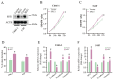
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a common malignancy in Southeast Asia, and in the Guangxi and Guangdong provinces of China. The spermatogenic transcription factor zip 1 (SPZ1) is a member of bHLH zip family, and promotes tumorigenesis in the liver, colon and breast tissues. However, the role of SPZ1 in the progression of NPC is unclear. In this study, we found that SPZ1 mRNA and protein levels were significantly upregulated in NPC tissues compared to the normal nasopharyngeal tissues. Furthermore, SPZ1 knockdown in NPC cell lines inhibited proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and invasion in vitro, and suppressed tumorigenesis in an in vivo model. On the other hand, SPZ1 overexpression facilitated the growth of NPC cells. Mechanistically, SPZ1-driven progression of NPC is dependent on the Wnt5a/interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling pathway. Consistent with this, IL-6 levels were significantly increased in NPC tissues and correlated positively with SPZ1 expression. Taken together, our findings suggest that SPZ1 mediates NPC progression through Wnt5a/IL-6 signaling, and the SPZ1/Wnt5a/IL-6 axis is a potential therapeutic target for NPC.
Keywords: SPZ1; Wnt5a; interleukin-6; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; tumorigenesis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Function of AXL and molecular mechanisms in regulation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Jun 28;47(6):685-697. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210786. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35837768 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
WNT5A promotes stemness characteristics in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells leading to metastasis and tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 30;6(12):10239-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3518. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25823923 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 4 (TRPV4) promotes tumorigenesis via NFAT4 activation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 22;9:1064366. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1064366. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36619170 Free PMC article.
-
bHLH-zip transcription factor Spz1 mediates mitogen-activated protein kinase cell proliferation, transformation, and tumorigenesis.Cancer Res. 2005 May 15;65(10):4041-50. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3658. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15899793
-
Transcription factor SPZ1 promotes TWIST-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and oncogenesis in human liver cancer.Oncogene. 2017 Aug;36(31):4405-4414. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.69. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28368406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wong K, Hui EP, Lo KW, Lam W, Johnson D, Li L. et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:679–695. - PubMed
-
- Chen YP, Chan A, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2019;394:64–80. - PubMed
-
- Petersson F. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a review. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2015;32:54–73. - PubMed
-
- He X, Ye M, Guo X, Pan Z, Zhang Z, He S. et al. Treatment outcome of patients with stages i-ii nasopharyngeal carcinoma after late course accelerated hyperfractionation radiotherapy alone. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:1058–1063. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

