FOXA1, induced by RC48, regulates HER2 transcription to enhance the tumorigenic capacity of lung cancer through PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 39440051
- PMCID: PMC11493013
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.100210
FOXA1, induced by RC48, regulates HER2 transcription to enhance the tumorigenic capacity of lung cancer through PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
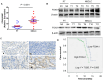
Lung cancer remains the tumor with the highest global incidence and mortality rates. Current primary treatment modalities encompass targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy; however, a subset of patients derives no benefit from these interventions. Recently, the HER2-targeting antibody drug Disitamab vedotin (RC48) was approved and introduced primarily for gastric and bladder cancers, with minimal investigation in the field of lung cancer. This study demonstrates that FOXA1 directly binds to the promoter region of HER2, influencing the HER2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which consequently modulates factors that foster lung cancer proliferation and impede apoptosis. Unlike FOXA1, HER2 does not influence the expression of FOXA1. Intriguingly, in lung cancer cells, RC48 not only impacts the HER2/PI3K/AKT pathway but also affects the FOXA1/HER2/PI3K/AKT pathway, thereby exerting a robust antitumor effect. In clinical specimens, heightened expressions of FOXA1 and HER2 correlate positively with clinical progression and poorer prognosis. These findings suggest that FOXA1 may serve as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target in future non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatments, and ongoing research may position RC48 as a transformative agent in lung cancer therapy.
Keywords: FOXA1; HER2; RC48; apoptosis.; proliferation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficacy of disitamab vedotin in non-small cell lung cancer with HER2 alterations: a multicenter, retrospective real-world study.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 6;14:1441025. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1441025. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39568568 Free PMC article.
-
Disitamab vedotin, a novel HER2-directed antibody-drug conjugate in gastric cancer and other solid tumors.Drugs Today (Barc). 2022 Oct;58(10):491-507. doi: 10.1358/dot.2022.58.10.3408812. Drugs Today (Barc). 2022. PMID: 36305543 Review.
-
Combined inhibition of HER2 and VEGFR synergistically improves therapeutic efficacy via PI3K-AKT pathway in advanced ovarian cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 26;43(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-02981-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38403634 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors enhanced the antitumor efficacy of disitamab vedotin for patients with HER2-positive or HER2-low advanced or metastatic gastric cancer: a multicenter real-world study.BMC Cancer. 2023 Dec 15;23(1):1239. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11735-z. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38102538 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR inhibitor introduce disitamab vedotin (RC48-ADC) rechallenge microtubule-chemotherapy resistance in HER2-low MBC patients with PI3K mutation.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 25;14:1312634. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1312634. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38344201 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FOXA1-mediated transcription of MFAP2 facilitates cell growth, metastasis and cisplatin resistance in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 28. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04041-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40153018
References
-
- Nasim F, Sabath BF, Eapen GA. Lung Cancer. The Medical clinics of North America. 2019;103:463–473. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Canales J, Parra-Cuentas E, Wistuba II. Diagnosis and Molecular Classification of Lung Cancer. Cancer treatment and research. 2016;170:25–46. - PubMed
-
- Landi L, Cappuzzo F. HER2 and lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2013;13(10):1219–28. - PubMed
-
- Mazières J, Peters S, Lepage B. et al. Lung cancer that harbors an HER2 mutation: epidemiologic characteristics and therapeutic perspectives. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:1997–2003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

