Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis Risk in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39440057
- PMCID: PMC11493017
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.100651
Development and Validation of a Nomogram for Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis Risk in Breast Cancer
Abstract
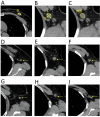
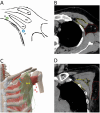
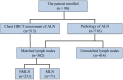
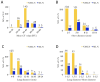
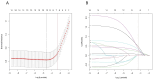
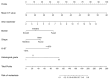
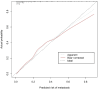
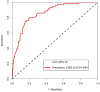
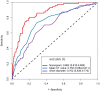
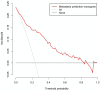
Purpose: Preoperative assessment of axillary lymph node (ALN) status is essential for breast cancer treatment planning. This study prospectively analyzed risk factors for ALN metastasis by comparing high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) imaging with pathology and developed a nomogram to aid in diagnosis. Methods: From April 2023 to May 2024, breast cancer patients confirmed by pathology participated in the study. All had chest HRCT before surgery, and ALN samples were anatomically matched to HRCT imaging and pathology. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression helped refine metastasis features, and a nomogram was constructed using the final selected features determined by multivariate logistic regression. The nomogram's performance was evaluated with concordance index (C-index), calibration plot, and decision curve analysis, with internal validation through bootstrapping. Results: A total of 302 ALN from 98 patients were included in this study. The predictors included in the nomogram encompassed the mean CT value, short diameter, border, and shape of ALN, as well as the Ki-67 status and histological grade of the primary tumor. The model exhibited satisfactory discrimination, with a C-index of 0.869 (95% CI: 0.826-0.912) and an AUC of 0.862 (95% CI, 0.815-0.909). The calibration curve demonstrated a high degree of concordance between the predicted and actual probabilities. The decision curve analysis demonstrated that the nomogram was clinically useful when the threshold for intervention was set at the metastasis possibility range of 1% to 86%. Conclusion: The nomogram combined with preoperative pathology and HRCT imaging have the potential to improve the evaluation of ALN status.
Keywords: Axillary lymph node; Breast cancer; HRCT; Metastasis; Nomogram.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H. et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–263. - PubMed
-
- Pilger TL, Francisco DF, Candido Dos Reis FJ. Effect of sentinel lymph node biopsy on upper limb function in women with early breast cancer: A systematic review of clinical trials. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021;47:1497–506. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

