Important functions and molecular mechanisms of aquaporins family on respiratory diseases: potential translational values
- PMID: 39440058
- PMCID: PMC11493008
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.98829
Important functions and molecular mechanisms of aquaporins family on respiratory diseases: potential translational values
Abstract
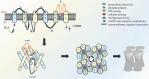
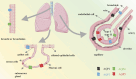
Aquaporins (AQPs) are a subgroup of small transmembrane transporters that are distributed in various types of tissues, including the lung, kidney, heart and central nervous system. It is evident that respiratory diseases represent a significant global health concern, with a considerable number of deaths occurring worldwide. Recent researches have demonstrated that AQPs play a pivotal role in respiratory diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In the context of NSCLC, the overexpression of AQP1, AQP3, AQP4, and AQP5 has been demonstrated to facilitate tumor angiogenesis, as well as the proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of tumor cells. This review concisely explores the role of AQP family on respiratory diseases, to assess their clinical and translational significance for understanding molecular pathogenesis. However, the potential translation of AQPs biomarkers into clinical applications is promising and the understanding of the precise mechanisms influencing respiratory diseases is still ongoing. Addressing the challenges and outlining the future perspectives in AQPs development is essential for clinical progress in a concise manner.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; aquaporins; bronchial asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; non-small cell lung cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aquaporins in sepsis- an update.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1495206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1495206. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporins in lung health and disease: Emerging roles, regulation, and clinical implications.Respir Med. 2020 Nov-Dec;174:106193. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106193. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33096317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporins: New players in breast cancer progression and treatment response.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 21;12:988119. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.988119. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36212456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aquaporins in Cancer Biology.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 29;12:782829. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.782829. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibodies to aquaporins are frequent in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017 Dec 1;56(12):2114-2122. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex328. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017. PMID: 28968830
Cited by
-
XGB-BIF: An XGBoost-Driven Biomarker Identification Framework for Detecting Cancer Using Human Genomic Data.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 11;26(12):5590. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125590. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565055 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of the AQP1 Gene Knockout on the Diversity, Composition and Function of Gut Microbiota in Mice with Heart Failure.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jul 4;14(7):815. doi: 10.3390/biology14070815. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723374 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

