An invisible-stylus-based coordinate measurement system via scaled orthographic projection
- PMID: 39440143
- PMCID: PMC11494961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2018.12.002
An invisible-stylus-based coordinate measurement system via scaled orthographic projection
Abstract
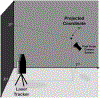
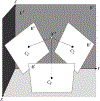
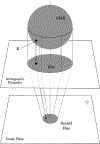
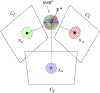
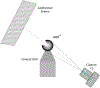
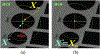
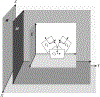
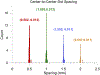
We present on a simple yet effective method for creating an invisible stylus from which a non-contact 3-D coordinated measuring system (the PiCMS) is realized. This invisible stylus dubbed a Pixel Probe is created through the orthographic projection of a spherical mounted reflector (SMR) through a trifocal camera system. Through this, a single point in space that is linked to a laser tracker world frame is mapped to a unique set of pixel coordinates in the trifocal camera creating the Pixel Probe. The system is constructed through the union of a Pixel Probe, a laser tracker, and calibrated stage, and does not require contact to obtain a measurement. In the current configuration, system resolution and accuracy better than is demonstrated on objects in the meso/micro scale that are well below the range of a laser tracker alone. A simple single-point coincidence condition allows the user to specify a measurement coordinate by pointing-and-clicking in the images captured by the Pixel Probe. We describe this system using multi-view geometry vision theory and present proof of concept measurement examples of 2-D and 3-D objects.
Keywords: Coordinate measuring machine; Laser tracker; Machine vision; Metrology; Non-contact; Probe; Spherical-mounted reflector.
Figures
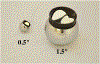






References
-
- Hocken JR, Pereira PH. Coordinate measuring machines and systems. second ed.CRC Press; 2016.
-
- Hocken RJ, Borchardt BR. On characterizing measuring machine geometry. NBSIR; 1979:79–1752.
-
- Stoup JR, Doiron TD. Accuracy and versatility of the NIST M48 coordinate measuring machine. Proc SPIE 2001;4401:136–46.
-
- Cuypers W, Gestel NV, Voet A, Kruth JP, Mingneau J, Bleys P. Optical measurement techniques for mobile and large-scale dimensional metrology. Optic Laser Eng 2009;47:292–300.
-
- Bqersad J, Poozesh P, Niezrecki C, Avitabile P. Photogrammetry and optical methods in structural dynamic-A review. Mech Syst Signal Process 2017;86:17–34.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
