Non-Invasive Ultrasound Diagnostic Techniques for Steatotic Liver Disease and Focal Liver Lesions: 2D, Colour Doppler, 3D, Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE), and Ultrasound-Guided Attenuation Parameter (UGAP)
- PMID: 39440161
- PMCID: PMC11494407
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.72087
Non-Invasive Ultrasound Diagnostic Techniques for Steatotic Liver Disease and Focal Liver Lesions: 2D, Colour Doppler, 3D, Two-Dimensional Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE), and Ultrasound-Guided Attenuation Parameter (UGAP)
Abstract
We conducted a comprehensive literature review to evaluate the efficacy of combining two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) and ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter (UGAP) in assessing the risk of progressive metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). This narrative review explores the applications of liver ultrasound in diagnosing metabolic liver diseases, focusing on recent advancements in diagnostic techniques for steatotic liver disease (SLD). Liver ultrasound can detect a spectrum of SLD manifestations, from metabolic dysfunction-associated liver disease (MASLD) to fibrosis and cirrhosis. It is also possible to identify inflammation, hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and various other liver lesions. Innovative ultrasound applications, including elastography and UGAP, can significantly enhance the diagnostic capabilities of ultrasound in accurately interpreting liver diseases. Understanding the pathogenesis of liver diseases requires a thorough analysis of their etiology and progression in order to develop sound diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Chronic liver diseases (CLD) vary in origin, with MASLD affecting approximately 20-25% of the general population. The insidious progression of CLD from inflammation to fibrosis and cirrhosis underscores the need for effective early detection methods. This review aims to highlight the evolving role of non-invasive ultrasound-based diagnostic tests in the early detection and staging of liver diseases. By synthesizing current evidence, we aim to provide an updated perspective on the utility of advanced ultrasound techniques in redefining the diagnostic landscape for metabolic liver diseases.
Keywords: liver ultrasound; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (mash); metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (masld); shear-wave ultrasonography; steatotic liver disease; two-dimensional shear wave elastography (2d-swe); ultrasound (u/s); ultrasound-guided attenuation parameter (ugap).
Copyright © 2024, Biris et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


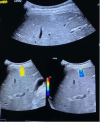
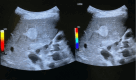
References
-
- Editorial on the current role of ultrasound. Dietrich CF, Sirlin CB, O’Boyle M, Dong Y, Jenssen C. App Sci. 2019;9:3512.
-
- Direct comparison of US and MR elastography for staging liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Imajo K, Honda Y, Kobayashi T, et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:908–917. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
