The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative-4 (ADNI-4) Engagement Core: A culturally informed, community-engaged research (CI-CER) model to advance brain health equity
- PMID: 39440702
- PMCID: PMC11667532
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14242
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative-4 (ADNI-4) Engagement Core: A culturally informed, community-engaged research (CI-CER) model to advance brain health equity
Abstract
Introduction: The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative-4 (ADNI-4) Engagement Core was launched to advance Alzheimer's disease (AD) and AD-related dementia (ADRD) health equity research in underrepresented populations (URPs). We describe our evidence-based, scalable culturally informed, community-engaged research (CI-CER) model and demonstrate its preliminary success in increasing URP enrollment.
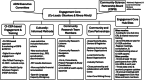
Methods: URPs include ethnoculturally minoritized, lower education (≤ 12 years), and rural populations. The CI-CER model includes: (1) culturally informed methodology (e.g., less restrictive inclusion/exclusion criteria, sociocultural measures, financial compensation, results disclosure, Spanish Language Capacity Workgroup) and (2) inclusive engagement methods (e.g., the Engagement Core team; Hub Sites; Community-Science Partnership Board).
Results: As of April 2024, 60% of ADNI-4 new in-clinic enrollees were from ethnoculturally or educationally URPs. This exceeds ADNI-4's ≥ 50% URP representation goal for new enrollees but may not represent final enrollment.
Discussion: Findings show a CI-CER model increases URP enrollment in AD/ADRD clinical research and has important implications for clinical trials to advance health equity.
Highlights: The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative-4 (ADNI-4) uses a culturally informed, community-engaged research (CI-CER) approach. The CI-CER approach is scalable and sustainable for broad, multisite implementation. ADNI-4 is currently exceeding its inclusion goals for underrepresented populations.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; cognitive aging; community‐engaged research; cultural humility; dementia; diversity; external validity; generalizability; health disparities; health equity; inclusion science; inclusive participation; underrepresented populations.
© 2024 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Please see submitted author ICJME disclosure forms. Author disclosures are available in the supporting information.
Figures
References
-
- Barnes LL, Wilson RS, Li Y, Gilley DW, Bennett DA, Evans DA. Change in cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease in African‐American and White persons. Neuroepidemiology. 2006;26(1):16‐22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

