A whole-cell pertussis vaccine engineered to elicit reduced reactogenicity protects baboons against pertussis challenge
- PMID: 39441011
- PMCID: PMC11580402
- DOI: 10.1128/msphere.00647-24
A whole-cell pertussis vaccine engineered to elicit reduced reactogenicity protects baboons against pertussis challenge
Abstract
Whole-cell pertussis (wP) vaccines introduced in the 1940s led to a dramatic reduction of pertussis incidence and are still widely used in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) worldwide. The reactogenicity of wP vaccines resulted in reduced public acceptance, which drove the development and introduction of acellular pertussis (aP) vaccines in high-income countries in the 1990s. Increased incidence of pertussis disease has been observed in high-income countries following the introduction of aP vaccines despite near universal rates of pediatric vaccination. These increases are attributed to the reduced protection against colonization, carriage, and transmission as well as reduced duration of immunity conferred by aP vaccines relative to the wP vaccines they replaced. A reduced reactogenicity whole-cell pertussis (RRwP) vaccine was recently developed with the goal of achieving the same protection as conferred by wP vaccination but with an improved safety profile, which may benefit countries in which wP vaccines are still in routine use. In this study, we tested the RRwP vaccine in a baboon model of pertussis infection. We found that the RRwP vaccine induced comparable cellular and humoral immune responses and comparable protection following challenge relative to the wP vaccine, while significantly reducing injection-site reactogenicity.IMPORTANCEThe World Health Organization (WHO) recommended in 2015 that countries administering wP vaccines in their national vaccine programs should continue to do so, and that switching to aP vaccines for primary infant immunization should only be considered if periodic booster vaccinations and/or maternal immunization could be assured and sustained in their national immunization schedules (WHO, Vaccine 34:1423-1425, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.136). Due to the considerably higher cost of aP vaccines and the larger number of doses required, most LMICs continue to use wP vaccines. The development and introduction of a wP vaccine that induces fewer adverse events without sacrificing protection would significantly benefit countries in which wP vaccines are still in routine use. The results of this study indicate this desirable goal may be achievable.
Keywords: baboon model; pertussis; whole cell vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

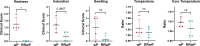
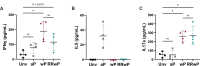

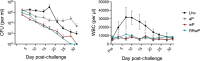
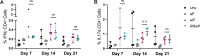

References
-
- Deloria MA, Blackwelder WC, Decker MD, Englund JA, Steinhoff MC, Pichichero ME, Rennels MB, Anderson EL, Edwards KM. 1995. Association of reactions after consecutive acellular or whole-cell pertussis vaccine immunizations. Pediatrics 96:592–594. - PubMed
-
- Barlow WE, Davis RL, Glasser JW, Rhodes PH, Thompson RS, Mullooly JP, Black SB, Shinefield HR, Ward JI, Marcy SM, DeStefano F, Chen RT, Immanuel V, Pearson JA, Vadheim CM, Rebolledo V, Christakis D, Benson PJ, Lewis N, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Vaccine Safety Datalink Working Group . 2001. The risk of seizures after receipt of whole-cell pertussis or measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine. N Engl J Med 345:656–661. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa003077 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Braun MM, Terracciano G, Salive ME, Blumberg DA, Vermeer-de Bondt PE, Heijbel H, Evans G, Patriarca PA, Ellenberg SS. 1998. Report of a US public health service workshop on hypotonic-hyporesponsive episode (HHE) after pertussis immunization. Pediatrics 102:E52. doi: 10.1542/peds.102.5.e52 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
