Cutaneous ureterostomy following robot-assisted radical cystectomy: a multicenter comparative study of transperitoneal versus retroperitoneal techniques
- PMID: 39441314
- PMCID: PMC11499339
- DOI: 10.1007/s00345-024-05300-x
Cutaneous ureterostomy following robot-assisted radical cystectomy: a multicenter comparative study of transperitoneal versus retroperitoneal techniques
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate the differences in perioperative outcomes between transperitoneal and retroperitoneal techniques in cutaneous ureterostomy (CUS).
Methods: Between 2018 and 2023, 55 patients underwent CUS following robot-assisted radical cystectomy. Among the 55 patients, we compared 33 patients who underwent transperitoneal CUS (t-CUS) and 22 who underwent retroperitoneal CUS (r-CUS).
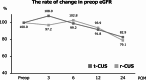
Results: Compared with the r-CUS group, the t-CUS group had significantly shorter operative times (p < 0.001); significantly less estimated blood loss (p < 0.001); and significantly lower incidence of complications (Clavien-Dindo classification grade ≤ 2) within 30 days (p = 0.005). Unexpectedly, the incidence of ileus within 30 days was lower, though the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.064). During the median follow-up period of 24.3 months, no ileus was observed in either group after 30 days postoperatively. There was no significant difference in the stent-free rate between the groups (p = 0.449). There were also no significant differences in the rates of change in estimated glomerular filtration rate from preoperatively at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months postoperatively between the groups (p = 0.590, p = 0.627, p = 0.741, and p = 0.778, respectively).
Conclusions: Compared with r-CUS, t-CUS was associated with a shorter operative time and lower incidence of perioperative complications, including gastrointestinal complications. We believe that t-CUS can be performed safely and effectively.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Cutaneous ureterostomy; Retroperitoneal technique; Robot-assisted radical cystectomy; Transperitoneal technique.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Burkhard FC, Wuethrich PY (2016) Cutaneous ureterostomy: ‘back to the future’. BJU Int 118:493–494. 10.1111/bju.13532 - PubMed
-
- Parekh DJ, Reis IM, Castle EP, Gonzalgo ML, Woods ME, Svatek RS et al (2018) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer (RAZOR): an open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 391:2525–2536. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30996-6 - PubMed
-
- Sasaki Y, Daizumoto K, Fukuta K, Shiozaki K, Nishiyama M, Utsunomiya S et al (2023) Lymph node dissection during radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a two-center comparative study of robotic versus open surgery. Asian J Endosc Surg 16:724–730. 10.1111/ases.13234 - PubMed
-
- Sasaki Y, Fukuta K, Kadoriku F, Daizumoto K, Shiozaki K, Tomida R et al (2024) Retroperitoneal cutaneous ureterostomy following radical cystectomy: a multicenter comparative study of robotic versus open surgery. Int J Urol [Internet]. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/iju.15580 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

