Potential Predictive Value of Platelet Distribution Width for Functional Outcome After Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 39441329
- PMCID: PMC11880176
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-024-04556-z
Potential Predictive Value of Platelet Distribution Width for Functional Outcome After Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
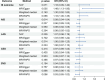
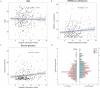
Complete blood cell count (CBC) is the most common and readily available laboratory test in clinical practice. The relationships of some CBC indices with ischemic stroke have been reported in observational studies; however, the causal direction is not specified. This study aimed to explore the causal relationships between CBC indices and the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score at 3 months after ischemic stroke. Genetic associations of 22 blood cell traits were obtained from the UK Biobank database (n = 350,475). The outcome data for ischemic stroke were obtained from the Genetic Ischemic Stroke Functional Outcome (GISCOME) network (n = 6021). We implemented two-sample Mendelian randomization (TSMR) and several complementary analyses to assess the causal association between blood traits and unfavorable outcome (3-month mRS > 2). The clinical cohort was validated based on the results of the MR analysis. TSMR result indicated causal association between genetically determined platelet distribution width (PDW) and adverse functional outcome after ischemic stroke (OR 1.48; 95% CI 1.13-1.95; p = 0.005). Complementary analyses showed negligible causal effect of genetic variants on stroke subtypes. In cohort study (n = 351), higher level of PDW was observed in the unfavorable outcome group. However, the multivariable logistic regression analysis failed to identify the improvement in predictive performance of stroke outcomes by adding PDW to the prediction model. Further correlation analysis revealed that PDW is positively correlated with serum glucose levels, and the level of PDW in the non-thrombolysed group was significantly higher than that in the thrombolysis group, indicating that PDW may be involved in stroke prognosis in an indirect way.
Keywords: Complete blood cell count; Functional outcome; Ischemic stroke; Mendelian randomization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: All the original GWAS studies had obtained relevant ethical approval and informed consent. Cohort study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, China. Consent to Participate: Written informed consent was obtained from all the participants or their immediate family members. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

