Radioanatomical evaluation of the subtympanic sinus in children under five years old and its clinical implications - high resolution computed tomography study
- PMID: 39441351
- PMCID: PMC11579157
- DOI: 10.1007/s00276-024-03508-5
Radioanatomical evaluation of the subtympanic sinus in children under five years old and its clinical implications - high resolution computed tomography study
Abstract
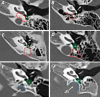
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate subtympanic sinus (STS) and its vicinity in high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans of children under five years old with non-diseased temporal bones.
Material and method: We divided the whole group into children under 24 months of age (first stage of pneumatisation development) and between 25 and 60 (second stage). We have determined the width of the entrance to STS, depth of the STS, type in relation to facial nerve according to Anschuetz classification, the pneumatisation of posterior and medial air cell tracts, and jugular bulb position. All the HRCTs (280 temporal bones) were analyzed according to the multiplanar reconstruction protocol with symmetrization.
Results: STS's mean width and depth were 2.71 ± 0.60 mm and 3.26 ± 1.11 mm, respectively. The most common STS type was type A (59.3%), followed by type B (30.7%) and type C (10%). The posterior air cell tract (retrofacial cells) was present in 39.3%. The medial air cell tract (hypotympanic cells) was present in 30.7% The jugular bulb position affected the final shape of STS in 17.5%.
Conclusion: The results support the necessity of the classification for the STS. Our study may help with surgical planning regarding endoscopic ear procedures and gives a broader understanding of how pneumatization or jugular bulb might correlate with the final shape of the retrotympanum. The historical remarks track the term's origin for clarity in research and respect for earlier investigators.
Keywords: Endoscopic ear surgery; Middle ear; Retrotympanum; Subtympanic sinus; Temporal bone; Temporal bone computed tomography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Medical University of Warsaw (decision number: AKBE/187/2019), and abides by the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
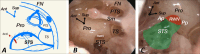


Similar articles
-
Novel Surgical and Radiologic Classification of the Subtympanic Sinus: Implications for Endoscopic Ear Surgery.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jul 10;159(6):194599818787180. doi: 10.1177/0194599818787180. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018. PMID: 29989841
-
On the radiologic anatomy of pediatric sinus tympani: HRCT study.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2022 Aug;49(4):606-612. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2021.11.004. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2022. PMID: 34844809
-
Radiologic evaluation and clinical assessment of facial sinus in adults and children - computed tomography study.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2024 Feb;51(1):189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2023.06.003. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2024. PMID: 37330319
-
Sinus tympani revisited for planning retrofacial approach-radiologic study in pneumatized temporal bones and its surgical implications.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Mar;280(3):1089-1099. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07576-4. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 35931824 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomy of the temporal bone.Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1998 Feb;8(1):195-209. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1998. PMID: 9449760 Review.
Cited by
-
The posterior-inferior recess of the sinus tympani - radioanatomical investigation for purposes of endoscopic otosurgery in children under five.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jul 12. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09558-8. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40652133
References
-
- Alicandri-Ciufelli M, Fermi M, Bonali M, Presutti L, Marchioni D, Todeschini A, Anschuetz L (2018) Facial sinus endoscopic evaluation, radiologic assessment, and classification. Laryngoscope 128:2397–2402. 10.1002/lary.27135 - PubMed
-
- Allam AF (1969) Pneumatization of the temporal bone. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 78(1):49–64. 10.1177/000348946907800105. PMID: 5763190 - PubMed
-
- Anschuetz L, Alicandri-Ciufelli M, Bonali M, Fermi M, Caversaccio M, Presutti L, Marchioni D (2018) Novel Surgical and Radiologic Classification of the Subtympanic Sinus: Implications for Endoscopic Ear Surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 10;159(6):194599818787180. 10.1177/0194599818787180. PMID: 29989841 - PubMed
-
- Baklaci D, Kuzucu I, Guler I, Akbal S, Kum NY, Yildirim GK, Parlak IS, Kum RO, Ozcan M (2019) Effect of mastoid bone pneumatization on the conformation and depth of the sinus tympani, a high-resolution computed tomography study. Surg Radiol Anat 41(8):921–926. 10.1007/s00276-019-02246-3 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

