Effect of 5β-dihydrotestosterone on vasodilator function and on cell proliferation
- PMID: 39441776
- PMCID: PMC11498709
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312080
Effect of 5β-dihydrotestosterone on vasodilator function and on cell proliferation
Abstract
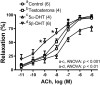
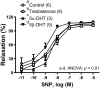
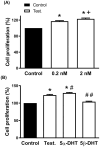
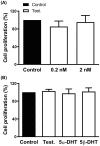
Aging is one of the main factors associated with cardiovascular diseases. Androgens exert beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system and testosterone (TES) replacement therapy improves cardiometabolic risk factors. However, TES is contraindicated in patients with prostate cancer due to its proliferative effects on prostatic tumor cells. Additionally, TES and its reduced metabolites 5α- and 5β-dihydrotestosterone (5α-DHT and 5β-DHT) exert vasodilatory effects. Since androgen levels decrease during aging and 5β-DHT lacks genomic effects, this study is focused on analyzing its effect on vasodilator function and the proliferation rate of prostatic tumor and vascular smooth muscle cells. To study the vascular function, mesenteric arteries from aged-orchidectomized Sprague-Dawley rats were used. Mesenteric segments were divided into one control (without treatment) and three groups with the androgens (10 nM, 30 min) to analyze: acetylcholine- and sodium nitroprusside-induced responses and nitric oxide and superoxide anion production. To analyze cell proliferation, the effect of androgens on cell viability was determined. The results showed that 5β-DHT improves vasodilator function in arteries from aged-orchidectomized rats and induces antioxidant action, while the proliferation rate of the androgen-dependent prostatic tumor cells remains unaltered. These results make 5β-DHT a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of cardiovascular pathologies.
Copyright: © 2024 Sánchez-Fernández et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- del Campo M, Sagredo A, del Campo L, Villalobo A, Ferrer M. Time-Dependent Effect of Orchidectomy on Vascular Nitric Oxide and Thromboxane A2 Release. Functional Implications to Control Cell Proliferation through Activation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. PLoS One. 2014;9: e102523-. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102523 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

