Prolonging the circulatory half-life of C1 esterase inhibitor via albumin fusion
- PMID: 39441778
- PMCID: PMC11498661
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305719
Prolonging the circulatory half-life of C1 esterase inhibitor via albumin fusion
Abstract
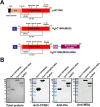
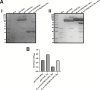
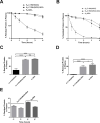
Hereditary Angioedema (HAE) is an autosomal dominant disease characterized by episodic swelling, arising from genetic deficiency in C1-esterase inhibitor (C1INH), a regulator of several proteases including activated Plasma kallikrein (Pka). Many existing C1INH treatments exhibit short circulatory half-lives, precluding prophylactic use. Hexahistidine-tagged truncated C1INH (trC1INH lacking residues 1-97) with Mutated N-linked Glycosylation Sites N216Q/N231Q/N330Q (H6-trC1INH(MGS)), its murine serum albumin (MSA) fusion variant (H6-trC1INH(MGS)-MSA), and H6-MSA were expressed in Pichia pastoris and purified via nickel-chelate chromatography. Following intravenous injection in mice, the mean terminal half-life of H6-trC1INH(MGS)-MSA was significantly increased versus that of H6-trC1INH(MGS), by 3-fold, while remaining ~35% less than that of H6-MSA. The extended half-life was achieved with minimal, but significant, reduction in the mean second order rate constant of Pka inhibition of H6-trC1INH(MGS)-MSA by 33% relative to that of H6-trC1INH(MGS). Our results validate albumin fusion as a viable strategy for half-life extension of a natural inhibitor and suggest that H6-trC1INH(MGS)-MSA is worthy of investigation in a murine model of HAE.
Copyright: © 2024 Sivananthan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extension of the circulatory half-life of recombinant ecallantide via albumin fusion without loss of anti-kallikrein activity.J Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 10;391:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2024.06.002. Epub 2024 Jun 4. J Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38844246
-
Recombinant human C1 esterase inhibitor for the treatment of hereditary angioedema due to C1 inhibitor deficiency (C1-INH-HAE).Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015 Mar;11(3):319-27. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.1012502. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25669442 Review.
-
Specific Targeting of Plasma Kallikrein for Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema: A Revolutionary Decade.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022 Mar;10(3):716-722. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.11.011. Epub 2021 Nov 25. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022. PMID: 34838707
-
sgp120 and the contact system in hereditary angioedema: A diagnostic tool in HAE with normal C1 inhibitor.Mol Immunol. 2020 Mar;119:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.01.003. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31955064
-
Treatment of Hereditary Angioedema.J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb;31(1):1-16. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0653. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33602658 Review.
References
-
- Landerman N.S., Webster M.E., Becker E.L. and Ratcliffe H.E., "Hereditary angioneurotic edema. II. Deficiency of inhibitor for serum globulin permeability factor and/or plasma kallikrein," J Allergy, 1962. 33: p. 330–41. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson V.H. and Evans R.R., "A Biochemical Abnormality in Herediatry Angioneurotic Edema: Absence of Serum Inhibitor of C’ 1-Esterase," Am J Med, 1963. 35: p. 37–44. - PubMed
-
- Davis A.E. 3rd, "C1 inhibitor and hereditary angioneurotic edema," Annu Rev Immunol, 1988. 6: p. 595–628. - PubMed
-
- Gregorek H., Kokai M., Hidvegi T., Fust G., Sabbouh K. and Madalinski K., "Concentration of C1 inhibitor in sera of healthy blood donors as studied by immunoenzymatic assay," Complement Inflamm, 1991. 8(5–6): p. 310–2. - PubMed
-
- Huber R. and Carrell R.W., "Implications of the three-dimensional structure of alpha 1-antitrypsin for structure and function of serpins," Biochemistry, 1989. 28(23): p. 8951–66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

