SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1.5 mRNA booster vaccination elicits limited mucosal immunity
- PMID: 39441905
- PMCID: PMC11542980
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adp8920
SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1.5 mRNA booster vaccination elicits limited mucosal immunity
Abstract
Current COVID-19 vaccines provide robust protection against severe disease but minimal protection against acquisition of infection. Intramuscularly administered COVID-19 vaccines induce robust serum neutralizing antibodies (NAbs), but their ability to boost mucosal immune responses remains to be determined. In this study, we show that the XBB.1.5 messenger RNA (mRNA) boosters result in increased serum neutralization to multiple severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants in humans, including the dominant circulating variant JN.1. In contrast, we found that the XBB.1.5 mRNA booster did not augment mucosal NAbs or mucosal IgA responses, although acute SARS-CoV-2 XBB infection substantially increased mucosal antibody responses. These data demonstrate that current XBB.1.5 mRNA boosters substantially enhance peripheral antibody responses but do not robustly increase mucosal antibody responses. Our data highlight a separation between the peripheral and mucosal immune systems in humans and emphasize the importance of developing next-generation vaccines to augment mucosal immunity to protect against respiratory virus infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
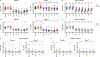


References
-
- Stankov MV, Hoffmann M, Gutierrez Jauregui R, Cossmann A, Morillas Ramos G, Graalmann T, Winter EJ, Friedrichsen M, Ravens I, Ilievska T, Ristenpart J, Schimrock A, Willenzon S, Ahrenstorf G, Witte T, Förster R, Kempf A, Pöhlmann S, Hammerschmidt SI, Dopfer-Jablonka A, Behrens GMN, Humoral and cellular immune responses following BNT162b2 XBB.1.5 vaccination. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 24, e1–e3 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, Guo Y, Bowen A, Mellis IA, Valdez R, Gherasim C, Gordon A, Liu L, Ho DD, XBB.1.5 monovalent mRNA vaccine booster elicits robust neutralizing antibodies against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. bioRxiv, 2023.2011.2026.568730 (2023).
-
- Chalkias S, McGhee N, Whatley JL, Essink B, Brosz A, Tomassini JE, Girard B, Edwards DK, Wu K, Nasir A, Lee D, Avena LE, Feng J, Deng W, Montefiori DC, Baden LR, Miller JM, Das R, Interim report of the reactogenicity and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 XBB-containing vaccines. J Infect Dis, (2024). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gayed J, Diya O, Lowry FS, Xu X, Bangad V, Mensa F, Zou J, Xie X, Hu Y, Lu C, Cutler M, Belanger T, Cooper D, Koury K, Anderson AS, Türeci Ö, Şahin U, Swanson KA, Modjarrad K, Gurtman A, Kitchin N, Safety and Immunogenicity of the Monovalent Omicron XBB.1.5-Adapted BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine in Individuals ≥12 Years Old: A Phase 2/3 Trial. Vaccines (Basel) 12, (2024). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

