Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Studies of New Thiazolidinone Derivatives as NNRTIs and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors
- PMID: 39442074
- PMCID: PMC11644116
- DOI: 10.1002/cbdv.202401697
Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Studies of New Thiazolidinone Derivatives as NNRTIs and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors
Abstract
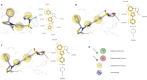
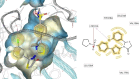
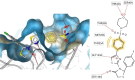
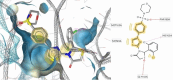
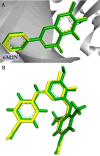
HIV-1 remains a major health problem worldwide since the virus has developed drug-resistant strains, so, the need for novel agents is urgent. The protein reverse transcriptase plays fundamental role in the viruses' replication cycle. FDA approved Delavirdine bearing a sulfonamide moiety, while thiazolidinone has demonstrated significant anti-HIV activity as a core heterocycle or derivative of substituted heterocycles. In this study, thirty new thiazolidinone derivatives (series A, B and C) bearing sulfonamide group were designed, synthesized and evaluated for their HIV-1 RT inhibition activity predicted by computer program PASS taking into account the best features of available NNRTIs as well as against SARS-COV-2 main protease. Seven compounds showed good anti-HIV inhibitory activity, with two of them, C1 and C2 being better (IC50 0.18 μΜ & 0.12 μΜ respectively) than the reference drug nevirapine (IC50 0.31 μΜ). The evaluation of molecules to inhibit the main protease revealed that 6 of the synthesized compounds exhibited excellent to moderate activity with two of them (B4 and B10) having better IC50 values (0.15 & 0.19 μΜ respectively) than the reference inhibitor GC376 (IC50 0.439 μΜ). The docking studies is coincides with experimental results, showing good binding mode to both enzymes.
Keywords: AIDS; COVID; HIV-1 reverse transcriptase; Molecular docking; SARS-CoV-2; Sulfonamides; Synthesis design; Thiazolidinone.
© 2024 The Author(s). Chemistry & Biodiversity published by Wiley-VHCA AG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
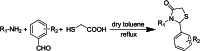
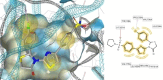
References
-
- UNAIDS/WHO estimates, 2023, HIV data and statistics. https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/s....
-
- Singh A. K., Kumar A., Arora S., Kumar R., Verma A., Khalilullah H., Jaremko M., Emwas A.-H., Kumar P., Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2024, 103, 14372–14393. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

