Epidermal stem cells: Interplay with the skin microenvironment during wound healing
- PMID: 39442652
- PMCID: PMC11625153
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mocell.2024.100138
Epidermal stem cells: Interplay with the skin microenvironment during wound healing
Abstract
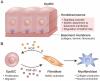
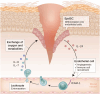
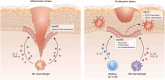
Skin undergoes everyday turnover while often challenged by injuries. The wound healing process in the skin is a dynamic sequence of events that involves various cell types and signaling pathways. Epidermal stem cells (EpdSCs), the tissue-resident stem cells in the skin tissue, are at the center of this complicated process due to their special ability to self-renew and differentiate. During this process, EpdSCs interact actively with the tissue microenvironment, which is essential for proper re-epithelialization and skin barrier restoration. This review describes the intricate interplays between EpdSCs and various components of their surroundings, including extracellular matrix/fibroblasts, vasculature/endothelial cells, and immune cells, as well as their roles in tissue repair.
Keywords: Epidermal stem cells; Re-epithelialization; Tissue microenvironment; Tissue repair; Wound healing.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson L.S., Yu S., Rivara K.R., Reynolds M.B., Hernandez A.A., Wu X., Yang H.Y., Isseroff R.R., Miller L.S., Hwang S.T., et al. CCR6+ γδ T cells home to skin wounds and restore normal wound healing in CCR6-deficient mice. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2019;139(9):2061–2064.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.02.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

