Advancements, challenges, and future prospects in clinical hyperpolarized magnetic resonance imaging: A comprehensive review
- PMID: 39442802
- PMCID: PMC12181021
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2024.100802
Advancements, challenges, and future prospects in clinical hyperpolarized magnetic resonance imaging: A comprehensive review
Abstract
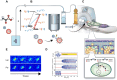
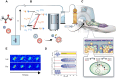
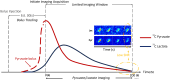
Hyperpolarized (HP) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a groundbreaking imaging platform advancing from research to clinical practice, offering new possibilities for real-time, non-invasive metabolic imaging. This review explores the latest advancements, challenges, and future directions of HP MRI, emphasizing its transformative impact on both translational research and clinical applications. By employing techniques such as dissolution Dynamic Nuclear Polarization (dDNP), Parahydrogen-Induced Polarization (PHIP), Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange (SABRE), and Spin-Exchange Optical Pumping (SEOP), HP MRI achieves enhanced nuclear spin polarization, enabling in vivo visualization of metabolic pathways with exceptional sensitivity. Current challenges, such as limited imaging windows, complex pre-scan protocols, and data processing difficulties, are addressed through innovative solutions like advanced pulse sequences, bolus tracking, and kinetic modeling. We highlight the evolution of HP MRI technology, focusing on its potential to revolutionize disease diagnosis and monitoring by revealing metabolic processes beyond the reach of conventional MRI and positron emission tomography (PET). Key advancements include the development of novel tracers like [2-13C]pyruvate and [1-13C]-alpha-ketoglutarate and improved data analysis techniques, broadening the scope of clinical metabolic imaging. Future prospects emphasize integrating artificial intelligence, standardizing imaging protocols, and developing new hyperpolarized agents to enhance reproducibility and expand clinical capabilities particularly in oncology, cardiology, and neurology. Ultimately, we envisioned HP MRI as a standardized modality for dynamic metabolic imaging in clinical practice.
Keywords: Carbon-13; Dynamic nuclear polarization; Hyperpolarization; Magnetic resonance imaging; Magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scalable Hyperpolarized MRI Enabled by Ace-SABRE of [1-13C]Pyruvate.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Apr 23:e202501231. doi: 10.1002/anie.202501231. Online ahead of print. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40268681
-
Positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the assessment of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2011 Jan;15(4):iii-iv, 1-134. doi: 10.3310/hta15040. Health Technol Assess. 2011. PMID: 21276372 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Diffuse High-Grade Gliomas: A Comprehensive Review Of Ad-vanced Methods Of Diagnosis And Treatment.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.2174/0115680096365252250618115641. Online ahead of print. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2025. PMID: 40598730
-
Current methods for hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI human studies.Magn Reson Med. 2024 Jun;91(6):2204-2228. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29875. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Magn Reson Med. 2024. PMID: 38441968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rhythms under tension: Circadian clocks in an Unsynced Society.Biomed J. 2025 Jun;48(3):100873. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2025.100873. Epub 2025 May 17. Biomed J. 2025. PMID: 40389157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Day SE, Kettunen MI, Gallagher FA, Hu D.-E, Lerche M, Wolber J, et al. Detecting tumor response to treatment using hyperpolarized 13C magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Nat Med. 2007;13(11):1382–1387. - PubMed
-
- Chen AP, Albers MJ, Cunningham CH, Kohler SJ, Yen Y-F, Hurd RE, et al. Hyperpolarized C-13 spectroscopic imaging of the TRAMP mouse at 3T—initial experience. Magn Reson Med. 2007;58(6):1099–1106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

