Dissecting the Conformational Heterogeneity of Stem-Loop Substructures of the Fifth Element in the 5'-Untranslated Region of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 39442924
- PMCID: PMC11544613
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c08406
Dissecting the Conformational Heterogeneity of Stem-Loop Substructures of the Fifth Element in the 5'-Untranslated Region of SARS-CoV-2
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Dissecting the Conformational Heterogeneity of Stem-Loop Substructures of the Fifth Element in the 5'-Untranslated Region of SARS-CoV-2".J Am Chem Soc. 2025 Feb 26;147(8):7158. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5c01923. Epub 2025 Feb 12. J Am Chem Soc. 2025. PMID: 39937987 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
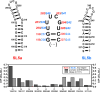
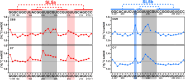
Throughout the family of coronaviruses, structured RNA elements within the 5' region of the genome are highly conserved. The fifth stem-loop element from SARS-CoV-2 (5_SL5) represents an example of an RNA structural element, repeatedly occurring in coronaviruses. It contains a conserved, repetitive fold within its substructures SL5a and SL5b. We herein report the detailed characterization of the structure and dynamics of elements SL5a and SL5b that are located immediately upstream of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF1a/b start codon. Exploiting the unique ability of solution NMR methods, we show that the structures of both apical loops are modulated by structural differences in the remote parts located in their stem regions. We further integrated our high-resolution models of SL5a/b into the context of full-length 5_SL5 structures by combining different structural biology methods. Finally, we evaluated the impact of the two most common VoC mutations within 5_SL5 with respect to individual base-pair stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures








References
-
- Wacker A.; Weigand J. E.; Akabayov S. R.; Altincekic N.; Bains J. K.; Banijamali E.; Binas O.; Castillo-Martinez J.; Cetiner E.; Ceylan B.; Chiu L.-Y.; Davila-Calderon J.; Dhamotharan K.; Duchardt-Ferner E.; Ferner J.; Frydman L.; Fürtig B.; Gallego J.; Grün J. T.; Hacker C.; Haddad C.; Hähnke M.; Hengesbach M.; Hiller F.; Hohmann K. F.; Hymon D.; de Jesus V.; Jonker H.; Keller H.; Knezic B.; Landgraf T.; Löhr F.; Luo L.; Mertinkus K. R.; Muhs C.; Novakovic M.; Oxenfarth A.; Palomino-Schätzlein M.; Petzold K.; Peter S. A.; Pyper D. J.; Qureshi N. S.; Riad M.; Richter C.; Saxena K.; Schamber T.; Scherf T.; Schlagnitweit J.; Schlundt A.; Schnieders R.; Schwalbe H.; Simba-Lahuasi A.; Sreeramulu S.; Stirnal E.; Sudakov A.; Tants J.-N.; Tolbert B. S.; Vögele J.; Weiß L.; Wirmer-Bartoschek J.; Wirtz Martin M. A.; Wöhnert J.; Zetzsche H. Secondary structure determination of conserved SARS-CoV-2 RNA elements by NMR spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48 (22), 12415–12435. 10.1093/nar/gkaa1013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manfredonia I.; Nithin C.; Ponce-Salvatierra A.; Ghosh P.; Wirecki T. K.; Marinus T.; Ogando N. S.; Snijder E. J.; van Hemert M. J.; Bujnicki J. M.; Incarnato D. Genome-wide mapping of SARS-CoV-2 RNA structures identifies therapeutically-relevant elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48 (22), 12436–12452. 10.1093/nar/gkaa1053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lan T. C. T.; Allan M. F.; Malsick L. E.; Woo J. Z.; Zhu C.; Zhang F.; Khandwala S.; Nyeo S. S. Y.; Sun Y.; Guo J. U.; Bathe M.; Näär A.; Griffiths A.; Rouskin S. Secondary structural ensembles of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome in infected cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13 (1), 1128.10.1038/s41467-022-28603-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

