Combined Administration of Metformin and Propionate Reduces the Degree of Oxidative/Nitrosative Damage of Hypothalamic Neurons in Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 39443349
- PMCID: PMC11880168
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-024-04529-2
Combined Administration of Metformin and Propionate Reduces the Degree of Oxidative/Nitrosative Damage of Hypothalamic Neurons in Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
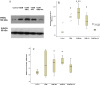
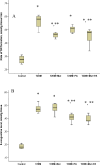
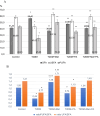
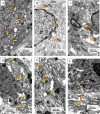
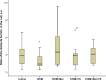
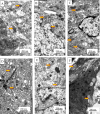
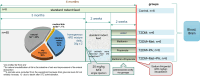
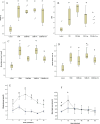
Many complications associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are closely linked with the generation of reactive species or free radicals leading to oxidative/nitrosative stress. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of combined administration of metformin with propionate on the degree of oxidative/nitrosative damage in the brain of rats with an experimental model of T2DM. Male Wistar rats were divided into control (healthy rats); rats with T2DM and no further therapy; rats with T2DM that received: metformin, propionate, propionate + metformin. Ventromedial hypothalamus samples were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy, gas-liquid chromatography, Western blotting, RT-PCR and electron paramagnetic resonance. Combined treatment resulted in normalization of the neuronal NOS levels and reduction of mRNA level of induced nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and superoxide radicals compared to untreated T2DM rats. A decrease was also observed in the level of 8-oxyguanine with normalization of fatty acids distribution. The combined treatment partially mitigated ultrastructural alterations resulting from oxidative/nitrosative damage in neurons' mitochondria in T2DM. Thus, we demonstrated a positive effect of the combined use of metformin and propionate on all indicators of oxidative/nitrosative stress in T2DM.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Metformin; Oxidative/Nitrosative stress; Propionate.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: The protocol of experiments on rats was approved by the Bioethics Committee of the Bogomolets National Medical University (Protocol No. 123 from 26/09/2022). Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

