Ductal lavage followed by observation versus oral corticosteroids in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: A randomized trial
- PMID: 39443446
- PMCID: PMC11500097
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53143-2
Ductal lavage followed by observation versus oral corticosteroids in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: A randomized trial
Abstract
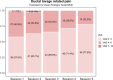
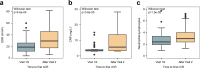
Oral corticosteroids represents the most prevalent treatment for idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Ductal lavage with triamcinolone acetonide and antibiotics followed by observation (DL-OBS) has emerged as a novel strategy, but a comparison of them remains lacking. Here in this multicenter, open-label, non-inferiority, randomized trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03724903), we assigned 140 patients to oral corticosteroids (N = 71) and DL-OBS (N = 69), stratified by baseline M-score. The primary outcome is complete Clinical Response rate at 1 year. The non-inferiority margin is -15%. The primary outcome is 85.5% in DL-OBS and 87.3% in oral corticosteroids (difference: -1.8%; 95%CI, 13.2 to 9.5; Pnon-inferiority = .01) in intention-to-treat population, and 92.6% vs 98.2% (difference -5.6%; 95%CI -13.4 to 2.2; Pnon-inferiority = .01) in per-protocol population, respectively. The most common (>15%) adverse events were Cushingoid, epigastric pain and arthralgia in oral corticosteroids, and irregular menstruation in DL-OBS, respectively. Here, we report that DL-OBS shows similar efficacy to oral corticosteroids but with better safety profile.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- #82271650/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- #202102010221/Guangzhou Science, Technology and Innovation Commission (Bureau of Science and Information Technology of Guangzhou Municipality)
- #SYS-Q-202002, #20180233/Sun Yat-sen University (SYSU)
- #2019A1515011467, #2019A1515110075 and #2021A1515012361/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Guangdong Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

