LncRNA MSTRG.13,871/miR155-5p/Grip1 network involved in the post-cardiac arrest brain injury
- PMID: 39443577
- PMCID: PMC11499652
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-75875-3
LncRNA MSTRG.13,871/miR155-5p/Grip1 network involved in the post-cardiac arrest brain injury
Abstract
Post-cardiac arrest brain (PCABI) is a severe medical condition characterized by a significant risk of neurological impairment and death. Nevertheless, the specific process and essential molecules responsible for its development are not fully understood. Profiling based on competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNA) has been implicated in the onset and progression of neurological disorders, yet its role in PCABI remains unclear. In this study, we performed RNA transcriptome sequencing analysis to identify differentially expressed genes in the rat model for cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CA/CPR). A hub ceRNA regulatory network was constructed using miRWalk 2.0 and Cytohubba plug-in in Cytoscape. Subsequently, real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and dual-luciferase activity assays validated MSTRG.13,871, miR-155-5p, and Grip1 as differentially expressed in CA/CPR group, with MSTRG.13,871 capable of targeting both miR-155-5p and Grip1. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analyses revealed the ceRNA network enrichment in immunoregulation mechanisms such as mitochondrion, apoptotic process, and negative regulation cell death. Our research highlights the mechanism of PCABI by revealing a critical regulatory axis involving MSTRG.13,871-miR-155-5p-Grip1 in the hippocampus CA1 region after CA/CPR in rats, proposing a feasible controlled mechanism, which may serve as a theoretical basis for designing innovative therapies.
Keywords: Hippocampus; LncRNA; MiR-155-5p; Post-cardiac arrest brain injury; cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
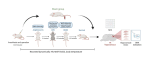
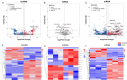

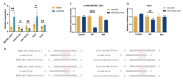
References
-
- Nesseler, N., Leurent, G. & Seguin, P. Neurologic prognosis after cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med 361, 1999; author reply 1999–2000 (2009). 10.1056/NEJMc091781 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2024ZL716/Zhejiang Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project
- 202204A10/Science and Technology Development Project of Hangzhou
- OO20200485/Construction Fund of Medical Key Disciplines of Hangzhou
- Z20220026/Medical and Health Technology Project of Hangzhou
- 82002008/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

