Large language model use in clinical oncology
- PMID: 39443582
- PMCID: PMC11499929
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00733-4
Large language model use in clinical oncology
Abstract
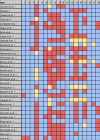
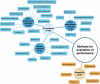
Large language models (LLMs) are undergoing intensive research for various healthcare domains. This systematic review and meta-analysis assesses current applications, methodologies, and the performance of LLMs in clinical oncology. A mixed-methods approach was used to extract, summarize, and compare methodological approaches and outcomes. This review includes 34 studies. LLMs are primarily evaluated on their ability to answer oncologic questions across various domains. The meta-analysis highlights a significant performance variance, influenced by diverse methodologies and evaluation criteria. Furthermore, differences in inherent model capabilities, prompting strategies, and oncological subdomains contribute to heterogeneity. The lack of use of standardized and LLM-specific reporting protocols leads to methodological disparities, which must be addressed to ensure comparability in LLM research and ultimately leverage the reliable integration of LLM technologies into clinical practice.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: T.J.B. would like to disclose that he is the owner of Smart Health Heidelberg GmbH (Handschuhsheimer Landstr. 9/1, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany;
Figures


References
-
- ChatGPT. https://openai.com/chatgpt.
-
- Microsoft Copilot. https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-copilot.
-
- Gemini. Gemini—Chat to Supercharge Your Ideashttps://gemini.google.com/ (2024).
-
- Meta Llama. Meta Llamahttps://llama.meta.com/ (2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

