Development and validation of an inflammation-nutrition indices-based nomogram for predicting early recurrence in patients with stage IB lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39443648
- PMCID: PMC11500178
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76230-2
Development and validation of an inflammation-nutrition indices-based nomogram for predicting early recurrence in patients with stage IB lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
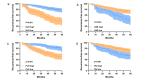
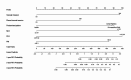
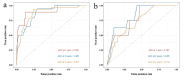
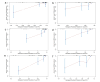
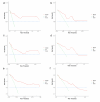
To explore the inflammation-nutrition indices and related clinical factors affecting early recurrence in patients with stage IB LUAD. A retrospective analysis was conducted on clinical and pathological data of patients diagnosed with stage IB LUAD who underwent radical surgery in our hospital from January 2016 to January 2021. Using R software, patients were randomly divided into training (n = 140) and validation (n = 59) cohorts in a 7:3 ratio. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed to identify risk factors for RFS and construct a predictive model. The performance of the model was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), concordance index (C-index), and calibration curve. Clinical utility of the model was assessed using decision curve analysis (DCA). Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that vascular invasion, visceral pleural invasion, predominant pattern, preoperative NLR > 2.33, preoperative PLR > 127.62, and preoperative PNI ≤ 48.3 were independent risk factors for RFS. The C-index of the nomogram model constructed based on these independent risk factors was 0.825 (95% CI: 0.762-0.881) in the training cohort and 0.772 (95% CI: 0.667-0.876) in the validation cohort. The ROC curves showed AUCs of 0.902, 0.881, and 0.877 for 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year RFS in the training cohort and AUCs of 0.782, 0.825, and 0.732 in the validation cohort respectively. Calibration curve and decision curve analysis indicated good clinical value of the model. The nomogram model based on inflammation-nutrition indices has predictive value for early recurrence in patients with stage IB LUAD.
Keywords: Early recurrence; Inflammation-nutrition indices; Nomogram; Stage IB lung adenocarcinoma.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

