Engineering Escherichia coli via introduction of the isopentenol utilization pathway to effectively produce geranyllinalool
- PMID: 39443997
- PMCID: PMC11515624
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-024-02563-2
Engineering Escherichia coli via introduction of the isopentenol utilization pathway to effectively produce geranyllinalool
Abstract
Background: Geranyllinalool, a natural diterpenoid found in plants, has a floral and woody aroma, making it valuable in flavors and fragrances. Currently, its synthesis primarily depends on chemical methods, which are environmentally harmful and economically unsustainable. Microbial synthesis through metabolic engineering has shown potential for producing geranyllinalool. However, achieving efficient synthesis remains challenging owing to the limited availability of terpenoid precursors in microorganisms. Thus, an artificial isopentenol utilization pathway (IUP) was constructed and introduced in Escherichia coli to enhance precursor availability and further improve terpenoid synthesis.
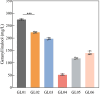
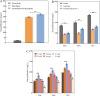
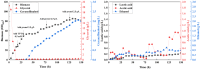
Results: We first constructed an artificial IUP in E. coli to enhance the supply of precursor geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) and then screened geranyllinalool synthases from plants to achieve efficient synthesis of geranyllinalool (274.78 ± 2.48 mg/L). To further improve geranyllinalool synthesis, we optimized various cultivation factors, including carbon source, IPTG concentration, and prenol addition and obtained 447.51 ± 6.92 mg/L of geranyllinalool after 72 h of shaken flask fermentation. Moreover, a scaled-up production in a 5-L fermenter was investigated to give 2.06 g/L of geranyllinalool through fed-batch fermentation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest reported titer so far.
Conclusions: Efficient synthesis of geranyllinalool in E. coli can be achieved through a two-step pathway and optimization of culture conditions. The findings of this study provide valuable insights into the production of other terpenoids in E. coli.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; Biosynthesis; Geranyllinalool; Isopentenol utilization pathway.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Formighieri C, Melis A. Heterologous synthesis of geranyllinalool, a diterpenol plant product, in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;101:2791–800. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Halitschke R, Li D, Paetz C, Su H, Heiling S, et al. Controlled hydroxylations of diterpenoids allow for plant chemical defense without autotoxicity. Science. 2021;371:255–60. - PubMed
-
- Svatoš A, Urbanová K, Valterová I. The first synthesis of Geranyllinalool Enantiomers. Collect Czech Chem Commun. 2002;67:83–90.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 232102311136, 232102320129 and 242102320122/the Key Research Projects of the Science and Technology Department of Henan Province
- 232102311136, 232102320129 and 242102320122/the Key Research Projects of the Science and Technology Department of Henan Province
- 110202102020/Key Research and Development Projects of Tobacco Corporation, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

