Preclinical and first-in-human evaluation of AL002, a novel TREM2 agonistic antibody for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 39444037
- PMCID: PMC11515656
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-024-01599-1
Preclinical and first-in-human evaluation of AL002, a novel TREM2 agonistic antibody for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
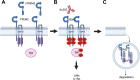
Background: Variants of the gene triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 (TREM2) increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative disorders. Signaling by TREM2, an innate immune receptor expressed by microglia, is thought to enhance phagocytosis of amyloid beta (Aβ) and other damaged proteins, promote microglial proliferation, migration, and survival, and regulate inflammatory signaling. Thus, TREM2 activation has potential to alter the progression of AD. AL002 is an investigational, engineered, humanized monoclonal immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibody designed to target TREM2. In AD mouse models, an AL002 murine variant has been previously shown to induce microglial proliferation and reduce filamentous Aβ plaques and neurite dystrophy.
Methods: Preclinical studies assessed the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of AL002 in cynomolgus monkeys. INVOKE-1 (NCT03635047) was a first-in-human phase 1, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study assessing the safety, tolerability, PK, and PD of AL002 administered as single ascending doses (SAD) in healthy volunteers.
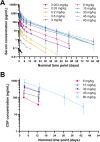
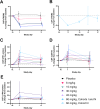
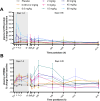
Results: In cynomolgus monkeys, weekly intravenous injections of AL002 for 4 weeks were well tolerated, dose-dependently decreased soluble TREM2 (sTREM2) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and total TREM2 in hippocampus and frontal cortex, and increased biomarkers of TREM2 signaling in CSF and brain. In the phase 1 study of 64 healthy volunteers, a single intravenous infusion of AL002 demonstrated brain target engagement based on a dose-dependent reduction of sTREM2 in CSF and parallel increases in biomarkers of TREM2 signaling and microglia recruitment. Single-dose AL002 showed central nervous system penetrance and was well tolerated, with no treatment-related serious adverse events over 12 weeks.
Conclusions: These findings support the continued clinical development of AL002 for AD and other neurodegenerative diseases in which TREM2 activation may be beneficial. AL002 is currently being tested in a phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in early AD.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, NCT03635047. Registered on August 15, 2018, https://www.
Clinicaltrials: gov/study/NCT03635047 .
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Biomarkers; Microglia; Phase 1 clinical trial; TREM2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
H.L., A.S., A.M., Br.B., T.N., Ba.B., An.R., and Ar.R. are employees of Alector, LLC and may have an equity interest in Alector, Inc. D.M., H.R., I.T., M.W., T.S., and R.P. were employees of Alector at the time of manuscript conception and may have an equity interest in Alector, Inc.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

