Tim-1-mediated extracellular matrix promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39444345
- PMCID: PMC11693869
- DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2024191
Tim-1-mediated extracellular matrix promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
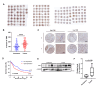
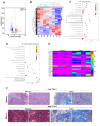
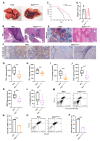
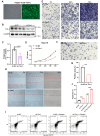
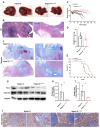
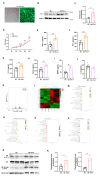
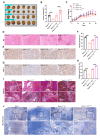
Tim-1 (T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 1), also known as Kim-1 (kidney injury molecule 1) or hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 1 (HAVCR1), is a transmembrane protein expressed on various immune and epithelial cells. It plays a role in modulating inflammatory and immune responses. In this study, we find that Tim-1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) samples and that its expression is significantly correlated with postoperative survival. Bulk RNA sequencing reveals a general upregulation of extracellular matrix-related genes in HCC tissues with Tim-1 overexpression. The results of the cell and in vivo experiments reveal that Tim-1 in HCC not only affects biological processes such as the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells but also broadly promotes extracellular matrix processes by influencing cytokine secretion. Further studies demonstrate that Tim-1 mediates the activation of hepatic stellate cells and upregulates Th1 and Th2 cytokines, thereby promoting HCC progression. Thus, Tim-1 may represent a novel target for future interventions in HCC and liver fibrosis.
Keywords: NF-κB; Tim-1; extracellular matrix; hepatocellular carcinoma; liver fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infiltrative Vessel Co-optive Growth Pattern Induced by IQGAP3 Overexpression Promotes Microvascular Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 May 15;30(10):2206-2224. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-2933. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38470497
-
Remodeling of hepatic stellate cells orchestrated the stroma-derived oxaliplatin-resistance through CCN3 paracrine in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2019 Dec 5;19(1):1192. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6362-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31805888 Free PMC article.
-
Tim-3/galectin-9 signaling pathway mediates T-cell dysfunction and predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2012 Oct;56(4):1342-51. doi: 10.1002/hep.25777. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22505239
-
Tim-3 expression and its role in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Oct 11;11(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0667-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30309387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic stellate cells and extracellular matrix in hepatocellular carcinoma: more complicated than ever.Liver Int. 2014 Jul;34(6):834-43. doi: 10.1111/liv.12465. Epub 2014 Feb 12. Liver Int. 2014. PMID: 24397349 Review.
References
-
- Filliol A, Schwabe RF. Contributions of fibroblasts, extracellular matrix, stiffness, and mechanosensing to hepatocarcinogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. . 2019;39:315–333. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1685539. - DOI - PubMed
-
- You Y, Zheng Q, Dong Y, Xie X, Wang Y, Wu S, Zhang L, et al. Matrix stiffness-mediated effects on stemness characteristics occurring in HCC cells. Oncotarget. . 2016;7:32221–32231. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8515. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tsuchida T, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. . 2017;14:397–411. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.38. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

