Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signalling Inhibition Suppresses Th1-Like Treg Generation by Reversing Mitochondrial Uncoupling
- PMID: 39444366
- PMCID: PMC11652410
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13870
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signalling Inhibition Suppresses Th1-Like Treg Generation by Reversing Mitochondrial Uncoupling
Abstract
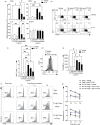
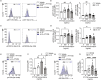
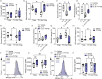
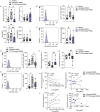
Inflammatory environments induce the generation of dysfunctional IFNγ+T-bet+FOXP3+ Th1-like Tregs, which show defective function and are found in autoimmune conditions including multiple sclerosis (MS). The pathways that control the generation of Th1-like Tregs are not well understood. Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) signalling molecules are upregulated in Th1-like Tregs, and in vivo S1P inhibition with Fingolimod (FTY720) inhibits the expression of genes responsible for Treg plasticity in MS patients. However, the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Here we show that S1P signalling inhibition by FTY720 inhibits the generation of Th1-like Tregs and rescues their suppressive function. These effects are mediated by a decrease in mTORC1 signalling and reversal of the mitochondrial uncoupling that Tregs undergo during their reprogramming into Th1-like Tregs in vitro. Finally, these results are validated in in vivo-generated Th1-like Tregs, as Tregs from MS patients treated with FTY720 display decreased Th1-like Treg frequency, increased suppressive function and mitochondrial metabolism rebalance. These results highlight the involvement of mitochondrial uncoupling in Treg reprogramming and identify S1P signalling inhibition as a target to suppress the generation of dysfunctional Th1-like Tregs.
Keywords: EAE/MS; Treg; autoimmunity.
© 2024 The Author(s). Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Komatsu N., Okamoto K., Sawa S., et al., “Pathogenic Conversion of Foxp3+ T Cells Into TH17 Cells in Autoimmune Arthritis,” Nature Medicine 20 (2014): 62–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

