ATP-induced reconfiguration of the micro-viscoelasticity of cardiac and skeletal myosin solutions
- PMID: 39444380
- PMCID: PMC11495876
- DOI: 10.1063/5.0224003
ATP-induced reconfiguration of the micro-viscoelasticity of cardiac and skeletal myosin solutions
Abstract
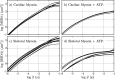
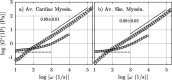
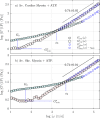
We study the high-frequency, micro-mechanical response of suspensions composed of cardiac and skeletal muscle myosin by optical trapping interferometry. We observe that in low ionic strength solutions, upon the addition of magnesium adenosine triphosphate (MgATP2-), myosin suspensions radically change their micro-mechanics properties, generating a viscoelastic fluid characterized by a complex modulus similar to a suspension of worm-like micelles. This transduction of energy, from chemical to mechanical, may be related to the relaxed states of myosin, which regulate muscle contractility and can be involved in the etiology of many myopathies. Within an analogous generic mechanical response, cardiac and skeletal myosin suspensions provide different stress relaxation times, elastic modulus values, and characteristic lengths. These discrepancies probably rely on the dissimilar physiological functions of cardiac and skeletal muscle, on the different MgATPase hydrolysis rates of cardiac and skeletal myosins, and on the observed distinct cooperative behavior of their myosin heads in the super-relaxed state. In vitro studies like these allow us to understand the foundations of muscle cell mechanics on the micro-scale, and may contribute to the engineering of biological materials whose micro-mechanics can be activated by energy regulators.
© 2024 Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Kovács M. and Málnási-Csizmadia A., “ Biophysical approaches to understanding the action of myosin as a molecular machine,” in Molecular Biophysics for the Life Sciences, edited by Allewell N., Narhi L. O., and Rayment I. ( Springer; New York, 2013), pp. 341–361.
-
- Harrington W. F., Rodgers E. R., and Davis J. S., “ Functional aspects of the myosin rod in contraction,” in Molecular Mechanisms in Muscular Contraction, edited by Squire J. M. ( Macmillan Education; UK, 1990), pp. 241–263.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
