Electrochemical detection of glutamate and histamine using redox-labeled stimuli-responsive polymer as a synthetic target receptor
- PMID: 39444408
- PMCID: PMC11498899
- DOI: 10.1021/acsapm.4c00121
Electrochemical detection of glutamate and histamine using redox-labeled stimuli-responsive polymer as a synthetic target receptor
Abstract
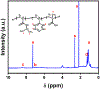
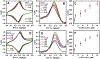
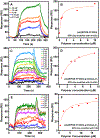
Glutamate (Glu) and histamine (His) are two major neurotransmitters that play many critical roles in brain physiological functions and neurological disorders. Therefore, specific and sensitive monitoring of Glu and His is essential in the diagnosis and treatment of various mental health and neurodegenerative disorders. Both being non-electroactive species, direct electrochemical detection of Glu and His has been challenging. Herein, we report a stimuli-responsive polymer-based biosensor for the electrochemical detection of Glu and His. The polymer-based target receptors consist of a linear chain stimuli-responsive templated polymer hybrid that is labeled with an osmium-based redox-active reporter molecules to elicit conformation-dependent electrochemical responses. The polymers are then attached to a gold electrode to implement an electrochemical sensor. The cyclic voltammetry (CV) and square-wave voltammetry (SWV) results confirmed the polymers' conformational changes due to the specific target (i.e., Glu and His) recognition and the corresponding electrochemical detection capabilities. The voltammetry results indicate that this biosensor can be used as a 'signal-on' and 'signal-off' sensors for the detection of Glu and His concentrations, respectively. The developed biosensor also showed excellent regeneration capability by fully recovering the initial current signal after rinsing with deionized water. To further validate the polymer's utility as a target bioreceptor, the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique was used to characterize the binding affinity between the designed polymers and the target chemical. The SPR results exhibited the equilibrium dissociation constants (KD) of 2.40 μM and 1.54 μM for the polymer-Glu and polymer-His interactions, respectively. The results obtained this work strongly suggest that the proposed sensing technology could potentially be used as a platform for monitoring non-electroactive neurochemicals from animal models.
Keywords: Electrochemical biosensor; Glutamate; Histamine; Neurotransmitters; SPR; Templated polymers.
Figures
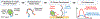
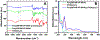
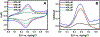

References
-
- Watanabe M; Akahoshi T; Tabata Y; Nakayama D Molecular Specific Swelling Change of Hydrogels in Accordance with the Concentration of Guest Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1998, 120 (22), 5577–5578. 10.1021/ja973070n. - DOI
-
- Park KS; Choi A; Kim HJ; Park I; Eom M-S; Yeo S-G; Son RG; Park T-I; Lee G; Soh HT; Hong Y; Pack SP Ultra-Sensitive Label-Free SERS Biosensor with High-Throughput Screened DNA Aptamer for Universal Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Variants from Clinical Samples. Biosens. Bioelectron 2023, 228, 115202. 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115202. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

