Ultrasensitive and highly selective Co2+ detection based on the chiral optical activities of L-glutathione-modified gold nanoclusters
- PMID: 39444637
- PMCID: PMC11496063
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1478021
Ultrasensitive and highly selective Co2+ detection based on the chiral optical activities of L-glutathione-modified gold nanoclusters
Abstract
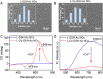
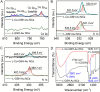
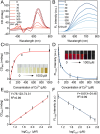
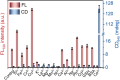
Developing highly sensitive and selective detection methods is crucial for environmental and healthcare monitoring. In this study, the chiral and fluorescent signals of L-glutathione-modified gold nanoclusters (L-GSH-Au NCs) were discovered to be responsive to Co2+, which displayed linear correlations with the concentration changes of Co2+. Notably, the chiral signal was more sensitive than the FL signal, whose limit of detection (LOD) was calculated to be 0.37 μM and 3.93 times lower than the LOD obtained with fluorescent signals. Moreover, the chiral signals exhibited unexpectedly high selectivity towards Co2+, effectively avoiding interference from other metal ions and biomolecules. Furthermore, the concentrations of Co2+ in various samples, such as Taihu water, tap water, bottled water, and animal serum, were accurately quantified using the chiral signals of L-GSH-Au NCs without complex pretreatment, with recoveries ranging between 95.64% and 103.22%. This study not only provides an innovative approach for Co2+ detection but also highlights the detection capabilities of chiral signals in complex environments.
Keywords: chirality; cobalt ion; detection; fluorescence; nanoclusters.
Copyright © 2024 Ding, Wang, Yang, Xing, Lin, Xu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hong A., Tang Q., Khan A. U., Miao M., Xu Z., Dang F., et al. (2021). Identification and speciation of nanoscale silver in complex solid matrices by sequential extraction coupled with inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 93 (4), 1962–1968. 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04741 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hussain M. M., Asiri A. M., Arshad M. N., Rahman M. M. (2018). Development of selective Co2+ ionic sensor based on various derivatives of benzenesulfonohydrazide (BSH) compound: an electrochemical approach. Chem. Eng. J. 339, 133–143. 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.130 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

