Unmet Medical Needs and Early Referral of Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis: An Expert Modified Delphi Consensus from Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 39444785
- PMCID: PMC11496595
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5636903
Unmet Medical Needs and Early Referral of Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis: An Expert Modified Delphi Consensus from Saudi Arabia
Abstract
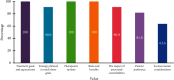
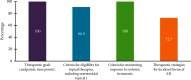
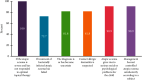
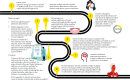
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic skin disease with increasing prevalence worldwide. It is characterized by pruritic eczematous lesions, affecting up to 20% of the children and negatively impacting their quality of life. Guidelines for AD management are available worldwide, but specific guidelines for pediatric AD in Saudi Arabia are lacking. This consensus document aims to identify the needs for the diagnosis and management of pediatric AD in Saudi Arabia by gathering the opinions and recommendations of key experts. We conducted a three-step modified Delphi method to develop the present consensus. The experts agreed that pediatricians and dermatologists commonly encounter AD; however, it is still under-recognized in its early stage in Saudi Arabia. The family physicians should be involved in assessing suspected children with a family history of atopy, particularly in patients with isolated lesions. Further, the experts confirmed that AD diagnosis should be documented, showing assessment criteria used, key morphological characteristics, and features used to ascertain the severity of the disease. There is still a need for simple validated diagnostic criteria suitable for daily practice for pediatric AD. The experts highlighted several medical conditions that pertain to the diagnosis and management of AD in Saudi Arabia.
Copyright © 2022 A. Alradaddi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Krakowski A. C., Eichenfield L. F., Dohil M. A. Management of atopic dermatitis in the pediatric population [Internet] . 2021;122:812–824. - PubMed
-
- McKenna S. P., Doward L. C. Current opinion in allergy and clinical immunology. Quality of life of children with atopic dermatitis and their families . 2021;8:228–231. - PubMed
-
- Weidinger S., Novak N. Atopic dermatitis. In: the lancet [internet] Lancet Publishing Group; 2016 . 2021:1109–1122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

