Ischemic Stroke: Pathophysiology and Evolving Treatment Approaches
- PMID: 39444789
- PMCID: PMC11497522
- DOI: 10.1177/26331055241292600
Ischemic Stroke: Pathophysiology and Evolving Treatment Approaches
Abstract
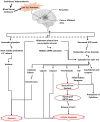
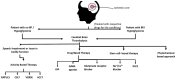
Stroke remains a leading cause of mortality and disability, with ischemic stroke being the most common type. It occurs due to reduced cerebral blood flow, leading to a cascade of events initiated by oxygen and nutrient deprivation, triggering excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation and finally culminating in neuronal injury and death. Key molecular players in ischemic stroke include glutamate receptors, acid-sensing ion channels, and purinergic receptors, exacerbating cellular damage through calcium influx, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Understanding these mechanisms has shaped therapeutic strategies, such as neuroprotective agents and stem cell therapies. Current treatments such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) emphasize timely intervention, yet challenges persist in patient-specific variability and accessibility. This review provides an overview of ischemic stroke pathophysiology, emphasizing cellular responses to ischemia and current and future therapeutic approaches including stem cell therapies aimed at mitigating stroke-induced disabilities and improving long-term outcomes.
Keywords: ASIC; Ischemic stroke; NMDA; ion channels; stroke therapy.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Hisham NF, Bayraktutan U. Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and treatment of hypertension in ischaemic stroke patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22:e4-14. - PubMed
-
- Jain M, Gupta S, Rijhwani P, et al. Prevalence of hemorrhagic stroke subtypes, etiological causes and its association with various stroke related risk factors: an observational study. J Mahatma J Univ Med Sci Technol. 2023;7:78-83.
-
- Unnithan A, Das J, Mehta P. Hemorrhagic Stroke. 2023. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

