The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
- PMID: 39444791
- PMCID: PMC11497216
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2024-1065
The chemoprotective hormetic effects of rosmarinic acid
Abstract
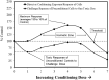
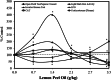
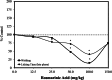
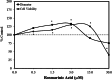
Rosmarinic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables, consumed in supplement form, and tested in numerous clinical trials for therapeutic applications due to its putative chemopreventive properties. Rosmarinic acid has been extensively studied at the cellular, whole animal, and molecular mechanism levels, presenting a complex array of multi-system biological effects. Rosmarinic acid-induced hormetic dose responses are widespread, occurring in numerous biological models and cell types for a broad range of endpoints. Consequently, this article provides the first assessment of rosmarinic acid-induced hormetic concentration/dose responses, their quantitative features, mechanistic foundations, extrapolative strengths/limitations, and their biomedical, clinical, and public health implications.
Keywords: U-shaped dose–response; biphasic dose response; dose–response; hormesis; neuroprotection.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. However, Vittorio Calabrese serves as Editor-in-Chief in Open Medicine, but this fact has not influenced the peer-review process.
Figures




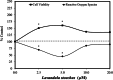
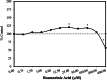






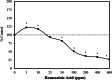
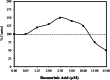
References
-
- Ravaria P, Saxena P, Laksmi S, Ranjan V, Abidi SWF, Saha P, et al. Molecular mechanisms of neuroprotective offerings by rosmarinic acid against neurodegenerative and other CNS pathologies. Phytother Res. 2023;37:2119–43. - PubMed
-
- Kopp-Schneider A, Lutz WK. J-shaped dose-response relationship for tumor induction by caffeic acid in the rat forestomach, modeled by non-monotonic dose response for DNA damage and cell proliferation. Hum Ecol Risk Assessment. 2001;7:921–31.
-
- Pietsch K, Saul N, Chakrabarti S, Sturzenbaum SR, Menzel R, Steinberg CEW. Formations, antioxidants and pro oxidants: defining curtain, caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid mediated life extension in C. elegans. Biogerontology. 2011;1-2:329–47. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
