Emerging role of microglia in inter-cellular transmission of α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39444806
- PMCID: PMC11496080
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1411104
Emerging role of microglia in inter-cellular transmission of α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
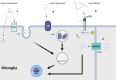
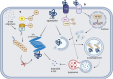
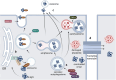
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide, significantly prejudicing the health and quality of life of elderly patients. The main pathological characteristics of PD are the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) as well as abnormal aggregation of α-synuclein (α-syn) monomers and oligomers, which results in formation of Lewy bodies (LBs). Intercellular transmission of α-syn is crucial for PD progression. Microglia play diverse roles in physiological and pathological conditions, exhibiting neuroprotective or neurotoxic effects; moreover, they may directly facilitate α-syn propagation. Various forms of extracellular α-syn can be taken up by microglia through multiple mechanisms, degraded or processed into more pathogenic forms, and eventually released into extracellular fluid or adjacent cells. This review discusses current literature regarding the molecular mechanisms underlying the uptake, degradation, and release of α-syn by microglia.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; microglia; neurodegeneration; propagation; α-synuclein.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Yu and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Afratis N., Nikitovic D., Multhaupt H., Theocharis A., Couchman J., Karamanos N. (2017). Syndecans - key regulators of cell signaling and biological functions. FEBS J. 284 27–41. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous