Profiling cytokines in peritoneal effluent through a targeted multiplex cytokine panel provides novel insight into the localized proinflammatory processes in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis
- PMID: 39444816
- PMCID: PMC11496082
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1463391
Profiling cytokines in peritoneal effluent through a targeted multiplex cytokine panel provides novel insight into the localized proinflammatory processes in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis
Abstract
Objectives: The number of relevant markers indicating local intraperitoneal inflammation in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis (PD) is limited. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the compatibility of peritoneal effluent (PE) for proteomic analysis and assess its potential utility in immunoprofiling studies.
Methods: This pilot study included six PD patients from the Peritoneal Dialysis Center, Department of Nephrology, Transplantology, and Internal Medicine in Szczecin, Poland. All patients were clinically stable, with no signs of infections or malignancy at the time of study. PE samples were collected during routine surveillance visits at the Peritoneal Dialysis Center. Proteomic analysis of the samples was conducted using the Olink® (Olink Proteomics AB, Uppsala, Sweden) Target 48 Cytokine panel.
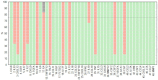
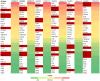
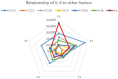
Results: PE samples were successfully analyzed, with 28 out of 45 proteins found within the limit of quantitation (LOQ) and 32 out of 45 proteins detected above the limit of detection (LOD). No significant interference from the matrix was observed in the assay. Biomarkers associated with low-grade inflammation showed varied levels, and the observed patterns were comparable across all patients.
Conclusion: This study suggests that utilizing a cytokine panel with relative quantification is a promising method for PE immunoprofiling.
Keywords: IL6; chronic kidney disease; effluent; inflammation; peritoneal dialysis; proteomics.
Copyright © 2024 Okulewicz, Wojciuk, Wojciechowska-Koszko, Domański and Gołembiewska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

