Bibliometric and knowledge map analysis of one lung ventilation
- PMID: 39444860
- PMCID: PMC11494552
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-645
Bibliometric and knowledge map analysis of one lung ventilation
Abstract
Background: One lung ventilation (OLV) is an essential method of lung isolation to protect the ventilated lung from soiling by the contralateral lung and obtain optimal surgical exposure in thoracic surgery. This study aims to examine the trends and developments in OLV research from 1982 to 2024 through bibliometric analysis.
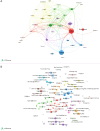
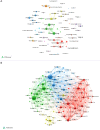
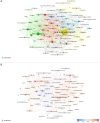
Methods: The literature on OLV was systematically searched in the Web of Science Core Collection database for this study. VOSviewer and CiteSpace were utilized to perform comprehensive bibliometric and visual analyses of global publication/trends, countries/institutions, authors/co-cited authors, journals/co-cited journals, co-cited references, and keywords in the field of OLV.
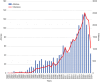
Results: A total of 1,682 articles and reviews on OLV research were identified, which showed an overall growing trend from 1982 to 2024. The United States was the leader in this field, accounting for the largest number of publications (n=299). Among all institutions, Yonsei University had the largest number of publications (n=23), but National Taiwan University Hospital had the highest number of cited publications (n=876). The papers related to OLV were mainly published in Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia (n=147) and the most productive author was Cheng YJ (n=15). After keywords analysis, "infants", "dexmedetomidine", "inflammation", and "airway management" were newly emergent research hotspots.
Conclusions: Through bibliometric and visualization methods, we undertook a comprehensive analysis in the field of OLV. The United States maintained a top position in this field, the emerging hotspots of OLV changed from basic research to clinical research and the further innovation of OLV management. This study provides new ideas for scholars in their future works.
Keywords: Airway management; bibliometric; one lung ventilation (OLV); visual analysis.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-645/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Ferrando C, Mugarra A, Gutierrez A, et al. Setting individualized positive end-expiratory pressure level with a positive end-expiratory pressure decrement trial after a recruitment maneuver improves oxygenation and lung mechanics during one-lung ventilation. Anesth Analg 2014;118:657-65. 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000105 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
