Chordoma combined with Trousseau syndrome: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 39444889
- PMCID: PMC11494589
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-1232
Chordoma combined with Trousseau syndrome: a case report and literature review
Abstract
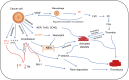
Background: Trousseau syndrome (TS) refers to spontaneous, recurrent, and wandering arterial and venous thromboembolic events in patients with tumors. It results from abnormalities in coagulation and fibrinolytic mechanisms of varying degrees throughout the course of the disease. It has a high fatality rate, and it is commonly seen in patients with highly invasive tumors, such as lung, pancreatic, gastrointestinal, and breast cancers; however, to date, there has been no report of TS combined with chordoma.
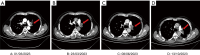
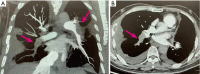
Case description: A 56-year-old male with a diagnosis of chordoma underwent surgery, immunotherapy, immunotherapy combined with antiangiogenic therapy, chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy, and proton therapy for localized metastases. Subsequent to the worsening of chest tightness, a repeat chest computed tomography angiography (CTA) scan suggested pulmonary artery embolisms; eventually, a diagnosis of TS was made. After anticoagulation and synchronized antitumor therapy, the patient's condition remained recurrent, eventually leading to death.
Conclusions: TS is a frequent but easily overlooked clinical complication that can occur in a variety of tumors, including chordoma, and is currently diagnosed clinically. Thus, further exploration of its sensitive markers is needed. We have reported a case of chordoma combined with TS and conducted a literature review on TS to increase clinicians' awareness of tumor-related thromboembolism and explore strategies to optimize the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of TS.
Keywords: Trousseau syndrome (TS); case report; chordoma; pulmonary embolism (PE); venous thrombosis.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-1232/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Melas N. Trousseau’s syndrome: a combination of cancer and hypercoagulability. Lakartidningen 2020;117:FTPY. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
