The prognostic factors of clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving subsequent treatments after progression on initial immunotherapy
- PMID: 39444890
- PMCID: PMC11494584
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-57
The prognostic factors of clinical outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving subsequent treatments after progression on initial immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: The standard of care for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients who encounter progression on initial immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) based treatment is uncertain. In the real world, there are various subsequent treatment options, but how to find the most suitable treatment for different patients is still unknown. The present study aimed to explore prognostic factors of subsequent treatment after progression (STAP) (defined as the next treatment after progression from the initial immunotherapy) of initial immunotherapy.
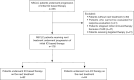
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, NSCLC patients received regimens after progression of initial immunotherapy at Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University, between March 2016 and May 2023 were retrieved. The major efficacy endpoint was progression-free survival 2 (PFS2), defined as the time from the initiation of next treatment after initial immunotherapy failure to disease progression or death from any cause. Subgroup analyses were conducted according to baseline characteristics, some subsequent regimens beyond progression, etc. for prognostic factors exploration. The Cox proportional hazards model was used for multivariate analysis.
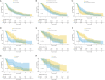
Results: There were 176 patients enrolled. Median age was 64 years. There were 36 (20.5%) females, and 123 (69.9%) were smokers. Adenocarcinoma (99, 56.2%) was the major histological subtype. There were 95 (54.0%) patients with negative expression for programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1). After progressive disease, 92 (52.3%) patients reused ICI-based treatment after progressive disease. Median PFS2 was 3.6 months [95% confidence interval (CI): 2.8-4.4]. Longer PFS2 was observed in patients with PD-L1 positive expression [hazard ratio (HR) =0.672, 95% CI: 0.477-0.947, P=0.023] or PFS ≥6 months in initial immunotherapy (HR =0.543, 95% CI: 0.358-0.824, P=0.004). Besides, patients switching to new ICI-based treatments without radiotherapy gained better PFS2 compared with patients receiving prior regimens (P=0.019).
Conclusions: PD-L1 positive expression, and longer PFS in initial immunotherapy would be good prognostic factors for NSCLC patients undergoing STAP on first immunotherapy. Besides, compared with original regimen, changing ICI would prolong PFS2 for NSCLC patients reusing ICI.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI); retreatment.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-57/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-based treatment beyond progression with prior immunotherapy in patients with stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective study.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Jun;11(6):1027-1037. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-376. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35832458 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor rechallenge in advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 Nov;148(11):3081-3089. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03901-2. Epub 2022 Jan 4. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34982222 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced lung cancer: Clinical characteristics, potential prognostic factors and next strategy.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 26;14:1089026. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1089026. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776868 Free PMC article.
-
Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 14;12(12):CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 30;4:CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub3. PMID: 33316104 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 30;4(4):CD013257. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013257.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33930176 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
