Does the guide sheath outperform the non-guide sheath method in endobronchial ultrasound-guided biopsy of peripheral pulmonary lesions?-a meta-analysis
- PMID: 39444910
- PMCID: PMC11494603
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-845
Does the guide sheath outperform the non-guide sheath method in endobronchial ultrasound-guided biopsy of peripheral pulmonary lesions?-a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)-guided transbronchial biopsy with or without a guide sheath (EBUS-GS or EBUS-nGS) is commonly utilized for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions (PPLs). The primary objective of this meta-analysis is to assess the diagnostic yield, surgical time, and safety of EBUS-GS and EBUS-nGS in patients presenting with PPLs, providing valuable insights for clinical decision-making.
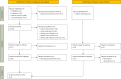
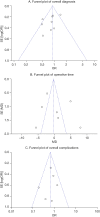
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of four databases (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library) up to January 2024. Two researchers independently screened the retrieved articles, extracted the data, assessed the quality of the studies, and conducted statistical analysis through Review Manager 5.4 and STATA 14.0. Subgroup analysis was used to explore potential sources of heterogeneity. Publication bias was assessed through funnel plot tests. Sensitivity analyses were also performed to evaluate the robustness of the combined results.
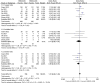
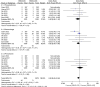
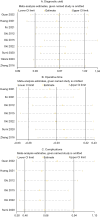
Results: The meta-analysis included data from nine studies comprising 2,898 patients. No publication bias was detected. There was no difference in the overall diagnostic rate of EBUS-GS and EBUS-nGS for PPLs [odds ratio (OR): 0.83, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.64-1.08, Z-score (Z) =1.37, P=0.17]. Conversely, in cases utilizing a bronchoscope with an outer diameter of 3.0 mm (OR: 0.58, 95% CI: 0.40-0.84, Z=2.86, P=0.004), a 1.7-mm bronchoscope channel (OR: 0.70, 95% CI: 0.51-0.96, Z=2.21, P=0.03), or lesions ≤30 mm in size, or lesions situated in the lower lobe of the lung (OR: 0.59, 95% CI: 0.38-0.91, Z=2.36, P=0.02), the diagnostic rate was higher in the EBUS-nGS group. However, the EBUS-GS group demonstrated a tremendous advantage in terms of safety (OR: 0.64, 95% CI: 0.44-0.93, Z=2.33, P=0.02).
Conclusions: EBUS-GS and EBUS-nGS showed no significant difference in the overall diagnostic rate for PPLs. When using a bronchoscope with an outer diameter of 3.0 mm or a channel diameter of 1.7 mm, or when lesions are ≤30 mm or located in the lower lobe of the lung, EBUS-nGS demonstrated a higher diagnostic rate, and EBUS-nGS demonstrated a higher diagnostic rate. However, EBUS-GS exhibited more tremendous advantages in terms of safety.
Keywords: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided biopsy (EBUS-guided biopsy); guide sheath (GS); meta-analysis; no guide sheath (nGS); peripheral pulmonary lesions (PPLs).
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-845/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Efficacy of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial biopsy without guide sheath for small peripheral pulmonary lesions (≤15 mm): A retrospective cohort study.Clin Respir J. 2021 Jun;15(6):622-627. doi: 10.1111/crj.13324. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Clin Respir J. 2021. PMID: 33394521
-
Radial endobronchial ultrasound - guided bronchoscopy for the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective trials.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 9;10(8):e29446. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29446. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38660275 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value and Safety of Addition of Transbronchial Needle Aspiration to Transbronchial Biopsy Through Endobronchial Ultrasonography Using a Guide Sheath Under Virtual Bronchoscopic Navigation for the Diagnosis of Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions.J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2024 Sep 13;31(4):e0984. doi: 10.1097/LBR.0000000000000984. eCollection 2024 Oct 1. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2024. PMID: 39268930
-
Endobronchial Ultrasonography With Guide Sheath for the Diagnosis of Peripheral Pulmonary Lesions in Japan: A Literature Review.Cureus. 2024 Mar 5;16(3):e55595. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55595. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38576679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided versus computed tomography-guided biopsy for peripheral pulmonary lesions: A meta-analysis.Clin Respir J. 2021 Jan;15(1):3-10. doi: 10.1111/crj.13275. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Clin Respir J. 2021. PMID: 32967044 Review.
Cited by
-
Radial Endobronchial Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Peripherally Located Pulmonary Lesions.Cureus. 2025 Jul 12;17(7):e87796. doi: 10.7759/cureus.87796. eCollection 2025 Jul. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40655061 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
