The relationship between stress, anxiety and eating behavior among Chinese students: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 39444958
- PMCID: PMC11496161
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1466700
The relationship between stress, anxiety and eating behavior among Chinese students: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The expansion of higher education and the growing number of college students have led to increased awareness of mental health issues such as stress, anxiety, and eating disorders. In China, the educational system and cultural expectations contribute to the stress experienced by college students. This study aims to clarify the role of anxiety as a mediator in the relationship between stress and eating behaviors among Chinese college students.
Methods: This study utilized data from the 2021 Psychology and Behavior Investigation of Chinese Residents, which included 1,672 college students under the age of 25. The analysis methods comprised descriptive statistics, t-tests, Pearson correlation analyses, and mediation effect analysis.
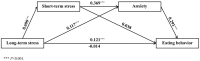
Results: The findings indicate that Chinese college students experience high levels of stress, with long-term stress slightly exceeding short-term stress. Both types of stress were positively correlated with increased anxiety and the adoption of unhealthy eating behaviors. Anxiety was identified as a significant mediator, accounting for 28.3% of the relationship between long-term stress and eating behavior (95% CI = 0.058-0.183). The mediation effect of short-term stress on eating behavior through anxiety was also significant, explaining 61.4% of the total effect (95% CI = 0.185-0.327).
Conclusion: The study underscores the importance of stress management and mental health services for college students. It recommends a comprehensive approach to reducing external pressures, managing anxiety, and promoting healthy eating behaviors among college students. Suggestions include expanding employment opportunities, providing career guidance, enhancing campus and societal support for holistic development, strengthening mental health services, leveraging artificial intelligence technologies, educating on healthy lifestyles, and implementing targeted health promotion programs.
Keywords: anxiety; college student; eating behavior; health psychology; stress.
Copyright © 2024 Chai, Fu, Liu, Song, Xue and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between problematic social media use and psychological distress among college students: a cross-sectional study in China exploring the mediating role of eating disorders.BMJ Open. 2025 May 21;15(5):e092863. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-092863. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40398952 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Eating and Its Relationship with Symptoms of Anxiety, Depression, and Stress During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multicenter Study in College Students.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Feb 27;22(3):354. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22030354. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40238407 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of cancer prevention education on the mental health of college students based on the difference-in-differences method.Front Public Health. 2024 Oct 8;12:1446225. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1446225. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39440181 Free PMC article.
-
Animal-assisted interventions in universities: a scoping review of implementation and associated outcomes.Health Promot Int. 2023 Jun 1;38(3):daac001. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daac001. Health Promot Int. 2023. PMID: 35092285
-
Materialism in Chinese college students during 2007-2020: The influence of social change on the inclining trend.Int J Psychol. 2025 Feb;60(1):e13260. doi: 10.1002/ijop.13260. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Int J Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39425580 Review.
Cited by
-
Patterns of lifestyle and their associations with anxiety symptoms among adolescents in Liaoning Province, China: a latent class analysis.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 8;13:1599214. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1599214. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40697840 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical