The influence of minimum dietary diversity on undernutrition among children aged 6-23 months in Ethiopia: a multilevel mixed-effect analysis based on 2019 Ethiopian mini demographic and health survey
- PMID: 39444959
- PMCID: PMC11496284
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1436683
The influence of minimum dietary diversity on undernutrition among children aged 6-23 months in Ethiopia: a multilevel mixed-effect analysis based on 2019 Ethiopian mini demographic and health survey
Abstract
Background: Undernutrition persists as a critical issue in developing countries like Ethiopia due to poor feeding practices for infants and young children. The impact of dietary diversity on children's health in Ethiopia remains unclear, necessitating further investigation to develop effective prevention strategies.
Objective: To examine the association between minimum dietary diversity and undernutrition among children aged 6-23 months in Ethiopia.
Methods: Data from the 2019 Ethiopian Mini Demographic and Health Survey, including 1,501 women with children aged 6-23 months, were analyzed using STATA version 17 software. Child stunting, wasting, and underweight were assessed using Z-scores. Dietary diversity was measured using minimum dietary diversity. Multilevel logistic regression analysis determined associations, presenting results as crude odds ratios (COR) and adjusted odds ratios (AOR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
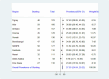
Results: Overall, 10.99% of children had adequate minimum dietary diversity, with Addis Ababa (44.57%) and Somalia (1.47%) showing the highest and lowest prevalences, respectively. The highest stunting prevalence was in the Amhara region (45.86%), while Addis Ababa had the lowest (9.78%). Wasting was lowest in Addis Ababa (1.09%) and highest in Tigray (17.07%). Underweight prevalence ranged from 2.17% in Addis Ababa to 33.33% in Tigray. Children with adequate minimum dietary diversity (MDD) had significantly lower odds of stunting (AOR = 0.68, 95% CI = 0.45, 0.96), underweight (AOR = 0.51, 95% CI = 0.27, 0.99), and wasting (AOR = 0.40, 95% CI = 0.17, 0.97) compared to those who had inadequate minimum dietary diversity (MDD).
Conclusion: This study highlights the association between minimum dietary diversity and stunting, wasting, and underweight among Ethiopian children aged 6-23 months. Urgent nutrition-specific interventions are needed, particularly in regions with high undernutrition rates and low dietary diversity. Targeted interventions focusing on promoting diverse and nutritious diets for children, along with improving access to essential healthcare services, are imperative to mitigate the burden of undernutrition and ensure the well-being of Ethiopia's youngest population and reinforcing existing programs is crucial to address this public health issue effectively.
Keywords: Ethiopia; children; dietary diversity; multilevel logistic regression; undernutrition.
Copyright © 2024 Shibeshi and Asfaw.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hanson K. The state and the world’s children. SAGE Publications: London, England; (2021). p. 3–7.
-
- Ba DM, Ssentongo P, Gao X, Chinchilli VM, Richie JP, Jr, Maiga M, et al. Prevalence and determinants of meeting minimum dietary diversity among children aged 6–23 months in three sub-Saharan African countries: the demographic and health surveys, 2019–2020. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:846049. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.846049, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belay DG, Aragaw FM, Teklu RE, Fetene SM, Negash WD, Asmamaw DB, et al. Determinants of inadequate minimum dietary diversity intake among children aged 6–23 months in sub-Saharan Africa: pooled prevalence and multilevel analysis of demographic and health survey in 33 sub-Saharan African countries. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:894552. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.894552, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

