The Sublingual Gland Flap for Oral Reconstruction: Insights From a Single Institutional Experience
- PMID: 39445029
- PMCID: PMC11498975
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/7386967
The Sublingual Gland Flap for Oral Reconstruction: Insights From a Single Institutional Experience
Abstract
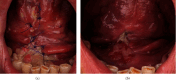
Background: Following ablative surgery, the reconstruction of oral cavity defects is essential to ensure optimal function and aesthetically acceptable outcomes. The purpose of this study was to retrospectively analyze the effectiveness and complication rates of the sublingual gland flap (SGF) in oral soft tissue reconstruction. The procedure for harvesting SGF and the strengths and limitations of the flap are discussed. Materials and Methods: The study group consisted of 13 patients suffering from oncological diseases who underwent soft tissue reconstruction with SGF. The patient's medical charts were evaluated based on histopathological aspects, postoperative complications, and outcomes. Reconstruction of the floor of the mouth was performed in 8 patients (61.5%) and lower gingiva in 5 patients (38.5%), respectively. Results: Complete epithelialization with closure of the defect was achieved within an average of 2 weeks. The observation period ranged from 1 to 33 months, with an average duration of 11.5 months. Partial flap necrosis and ranula occurred in one patient (7.7%). Furthermore, postoperative bleeding was observed in one patient (7.7%), and wound dehiscence and abscess formation were noted in another (7.7%). Locoregional recurrence of the cancer was observed in one case (7.7%). Conclusions: The SGF is effective for achieving successful reconstruction of small- and medium-sized defects in the lower gingiva and floor of the mouth. The complication rate is relatively low.
Keywords: local flap; oral cancer; reconstruction; sublingual gland; sublingual gland flap.
Copyright © 2024 Agata Wieczorkiewicz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

