Hypothalamic regulation of hippocampal CA1 interneurons by the supramammillary nucleus
- PMID: 39446584
- PMCID: PMC11644823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114898
Hypothalamic regulation of hippocampal CA1 interneurons by the supramammillary nucleus
Abstract
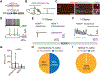
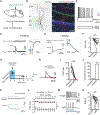
The hypothalamic supramammillary nucleus (SuM) projects heavily to the hippocampus to regulate hippocampal activity and plasticity. Although the projections from the SuM to the dentate gyrus (DG) and CA2 have been extensively studied, whether the SuM projects to CA1, the main hippocampal output region, is unclear. Here, we report a glutamatergic pathway from the SuM that selectively excites CA1 interneurons in the border between the stratum radiatum (SR) and the stratum lacunosum-moleculare (SLM). We find that the SuM projects selectively to a narrow band in the CA1 SR/SLM and monosynaptically excites SR/SLM interneurons, including vasoactive intestinal peptide-expressing (VIP+) and neuron-derived neurotrophic factor-expressing (NDNF+) cells, but completely avoids making monosynaptic contacts with CA1 pyramidal neurons (PNs) or parvalbumin-expressing (PV+) or somatostatin-expressing (SOM+) cells. Moreover, SuM activation drives spikes in most SR/SLM interneurons to suppress CA1 PN excitability. Taken together, our findings reveal that the SuM can directly regulate hippocampal output region CA1, bypassing CA2, CA3, and the DG.
Keywords: CA1; CA2; CP: Neuroscience; dentate gyrus; hippocampus; interneurons; neurogliaform cell; parvalbumin; stratum lacunosum-moleculare; supramammillary nucleus; vasoactive intestinal peptide.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

