Prevalence of visual impairment and its causes in adults aged 50 years and older: Estimates from the National Eye Surveys in Malaysia
- PMID: 39446766
- PMCID: PMC11500914
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299768
Prevalence of visual impairment and its causes in adults aged 50 years and older: Estimates from the National Eye Surveys in Malaysia
Abstract
Background: Population surveys are necessary to measure a community's eye care needs. We conducted simultaneous surveys in two regions in Malaysia in 2023 to estimate the prevalence of blindness and/or visual impairment (VI), identify its main causes, and compare the results with the survey in 2014.
Methods: The surveys were simultaneously done in Eastern and Sarawak administrative regions using the Rapid Assessment of Avoidable Blindness (RAAB) technique. It involved a multistage cluster sampling method, each cluster comprising 50 residents aged 50 years and older. The prevalence of blindness and/or visual impairment (blindness, severe, moderate, and early) and its primary cause were determined through a visual acuity test and eye examination with a hand-held ophthalmoscope. Results were compared with the previous survey in 2014.
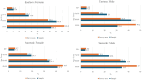
Results: A total of 10,184 subjects were enumerated, and 9,709 were examined (94.5% and 96.2% responses for Eastern and Sarawak, respectively). The prevalence of blindness and severe VI appeared lower than the previous survey. For blindness: Eastern 1.4%, 95%CI (0.9, 1.9) to 0.8%, 95%CI (0.5, 1.1) and Sarawak: 1.6% 95%CI (1.0, 2.1) to 0.6%, 95%CI (0.3, 0.9). For severe VI: Eastern 1.2%, 95%CI (0.8, 1.7) to 0.9%, 95%CI (0.6, 1.1) and Sarawak 1.1% 95%CI (0.6, 1.6) to 0.9%, 95% CI(0.6, 1.2). The main cause of blindness was untreated cataracts: 77.3% (Eastern) and 75.0% (Sarawak). Diabetic retinopathy was the 2nd main cause of blindness for Eastern at 9.1%, but it only caused early to severe VI in Sarawak.
Conclusion: The prevalence of blindness and severe VI were lower than in the previous survey. It could have been attributed to a community cataract program implemented soon after the survey in 2014. However, more efforts are needed to address the high percentage of avoidable blindness within both regions.
Copyright: © 2024 Salowi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO/IAPB Meeting on cataract surgery outcomes monitoring systems, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–20 September 2018: meeting report. URL:https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/who-325946.
-
- World Health Organization. Sixty-sixth World Health Assembly: Resolutions and decisions Annexes 2013.
-
- World Health Organization. Universal eye health: A global action plan 2014–2019. URL:https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/universal-eye-health-a-global action plan-2014-2019.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

