A fuzzy ontology-based case-based reasoning system for stomach dystemperament in Persian medicine
- PMID: 39446823
- PMCID: PMC11500847
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309722
A fuzzy ontology-based case-based reasoning system for stomach dystemperament in Persian medicine
Abstract
Background: In Persian medicine, early diagnosis and treatment of stomach dystemperament is crucial for preventing other diseases. However, traditional medicine diagnosis often involves ambiguous and less structured information making it challenging for practitioners. Integrating fuzzy ontology with case-based reasoning (CBR) systems can enhance diagnostic accuracy in this filed.
Objectives: This study aimed to develop and evaluate a fuzzy ontology-based CBR system for diagnosing and treating stomach dystemperament in Persian medicine.
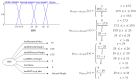
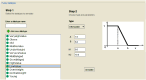
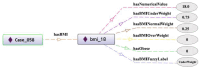
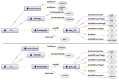
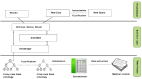
Methods: This was a mixed-methods research in which a fuzzy ontology-based CBR system was developed based on the fuzzy features, utilizing trapezoidal, triangular, right shoulder and left shoulder membership functions to represent linguistic variables such as hunger level and digestion power. The research phases included identifying relevant terms, concepts, and relationships, developing the fuzzy case-base ontology using the IKARUS-Onto methodology, and subsequently designing and implementing the CBR system. The system performance was evaluated in terms of its sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, precision, and F1-score.
Results: Initially, a case-base fuzzy ontology was created. Then, the database was built up using 88 expert-validated medical records. Of these cases, 72% (63 cases) were diagnosed with phlegmatic dystemperament, 18% (16 cases) with cold-dry dystemperament, and 10% (9 cases) had no stomach dystemperament. The CBR system was developed and evaluated using sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, precision, and F1-score which were 97.5%, 87.5%, 96.6%, 98.7%, and 98.1%, respectively.
Conclusions: Our fuzzy ontology-based CBR demonstrated high performance in diagnosing stomach dystemperament in Persian medicine. This system shows promise in improving diagnostic accuracy and facilitating the identification of similar cases. While initial results are encouraging, further evaluation in a real clinical environment is recommended to fully assess its practical utility.
Copyright: © 2024 Shojaee-Mend et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO traditional medicine strategy: 2014–2023. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/92455/1/9789_241506090eng.pdf.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO global report on traditional and complementary medicine 2019: World Health Organization; 2019.
-
- Zarei A, Rezaeizadeh H, Karimi M. Persian medicine perspective on the network between the liver and other organs. Hepatitis Monthly. 2021;21(11).
-
- Parsa E, Khodadoost M, Mokaberinejad R, Mojahedi M, Shirbeigi L, Zareiyan A, et al. Gastric dystemperament (sue-mizaj) in Iranian traditional medicine. Current Nutrition & Food Science. 2020;16(6):884–90.
-
- Chaichi-Raghimi M, Ilkhani R, Parsa E, Khodadoost M, Choopani R, Mokaberinejad R, et al. Major and minor criteria for gastric dystemperaments in Persian Medicine: Sari gastric dystemperament criteria-I (SGDC-I). Caspian Journal of Internal Medicine. 2022;13(4):681. doi: 10.22088/cjim.13.4.681 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

