A Nomogram Diagnostic Model for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction in Patients with Tympanic Membrane Perforation
- PMID: 39446836
- PMCID: PMC11514124
- DOI: 10.1177/19160216241293068
A Nomogram Diagnostic Model for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction in Patients with Tympanic Membrane Perforation
Abstract
Objectives: Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a common disease associated with chronic otitis media. A standard diagnostic tool for ETD in patients with tympanic membrane perforation is still lacking. We developed and validated a new diagnostic model for ETD in patients with tympanic membrane perforation.
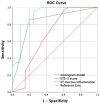
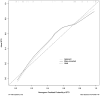
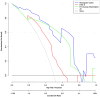
Methods: A prospective study was conducted in patients who had tympanic membrane perforation from February to August 2023. We collected clinical characteristics and examination results including otoscopy, nasal endoscopy, tubomanometry, and 5-item Eustachian Tube Score (ETS-5). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to determine the independent diagnostic factors. Based on this, the nomogram model was constructed. The discrimination and calibration of the nomogram were evaluated using the area under the curve (AUC), the C-index, the calibration curve, and the decision curve analysis (DCA).
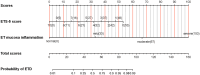
Results: A total of 40 participants were enrolled in the study. ETS-5 score and Eustachian tube opening mucosa inflammation in the nasopharynx were significant predictors in identifying ETD. Based on the above independent predictors, a diagnostic nomogram was successfully established. The sensitivity and specificity of the diagnostic model were 80.0% and 90.0%, respectively. The AUC and the C-index of the diagnostic model were both 0.901, which suggested that the model had a good discrimination power. The calibration curve indicated a good calibration degree of the model. DCA showed that the proposed model was useful for clinical practice.
Conclusion: The nomogram model is effective and reliable in identifying ETD in patients with tympanic membrane perforation.
Keywords: Eustachian tube dysfunction; chronic otitis media; diagnostic model; tympanic membrane perforation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

