Sprayable RNAi for silencing of important genes to manage red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
- PMID: 39446907
- PMCID: PMC11501036
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308613
Sprayable RNAi for silencing of important genes to manage red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae)
Abstract
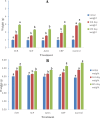
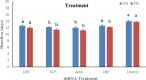
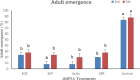
The red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Oliver, 1970) (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae) is the most devastating insect-pest of palm trees worldwide. Synthetic insecticides are the most preferred tool for the management of RPW. Alternatively, RNA interference (RNAi) mediated silencing of crucial genes provides reasonable control of insect pests. Recently, we have targeted four important genes; ecdysone receptor (EcR), serine carboxypeptidase (SCP), actin and chitin-binding peritrophin (CBP) in the 3rd and 5th instar larvae RPW. The results from 20 days trial showed that the survival rate of 3rd instar larvae fed on SCP and actin dsRNAs exhibited the lowest survival (12-68%). While, in the 5th instar larvae, the lowest survival rate (24%) was recorded for SCP after 20 days of incubation. Similarly, the weight of the 3rd and 5th instar larvae treated with SCP and actin was significantly reduced to 2.30-2.36 g and 4.64-4.78 g after 6 days of dsRNA exposure. The larval duration was also decreased significantly in the larvae treated with all the dsRNA treatments. The qRT-PCR results confirmed a significant suppression of the targeted genes as 90-97% and 85-93% in the 3rd and 5th instar larvae, respectively. The results suggest that the SCP and the actin genes can be promising targets to mediate RNAi-based control of RPW.
Copyright: © 2024 Sattar et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Dhehibi B, Salah MB, Frija A. Date palm value chain analysis and marketing opportunities for the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. In Agricultural Economics-Current Issues; IntechOpen; 2018.
-
- FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

