Conceptual Framework for Community-Based Prevention of Brown Dog Tick-Associated Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
- PMID: 39447135
- PMCID: PMC11521193
- DOI: 10.3201/eid3011.240293
Conceptual Framework for Community-Based Prevention of Brown Dog Tick-Associated Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Abstract
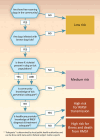
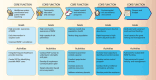
Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a severe tickborne disease that can reach epidemic proportions in communities with certain social and ecologic risk factors. In some areas, the case-fatality rate of brown dog tick-associated RMSF is up to 50%. Because of the spread of brown dog tick-associated RMSF in the southwestern United States and northern Mexico, the disease has the potential to emerge and become endemic in other communities that have large populations of free-roaming dogs, brown dog ticks, limited resources, and low provider awareness of the disease. By using a One Health approach, interdisciplinary teams can identify communities at risk and prevent severe or fatal RMSF in humans before cases occur. We have developed a conceptual framework for RMSF prevention to enable communities to identify their RMSF risk level and implement prevention and control strategies.
Keywords: Dermacentor species; Mexico; One Health; Rhipicephalus sanguineus; Rickettsia rickettsii; Rocky Mountain spotted fever; United States; bacteria; brown dog tick; health equity; tick-borne disease; ticks; vector-borne disease; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Severe and fatal confirmed Rocky Mountain spotted fever among people with recent travel to Tecate, Mexico. 2023. [cited 2023 Dec 8]. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/136450
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Rocky Mountain spotted fever in Mexico. [cited 2023 Dec 13]. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/notices/level1/rmsf-mexico
-
- Bustamante ME, Varela G. Una Nueva Rickettsiosis en Mexico. Rev Inst Salubr Enferm Trop. 1943;•••:4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

